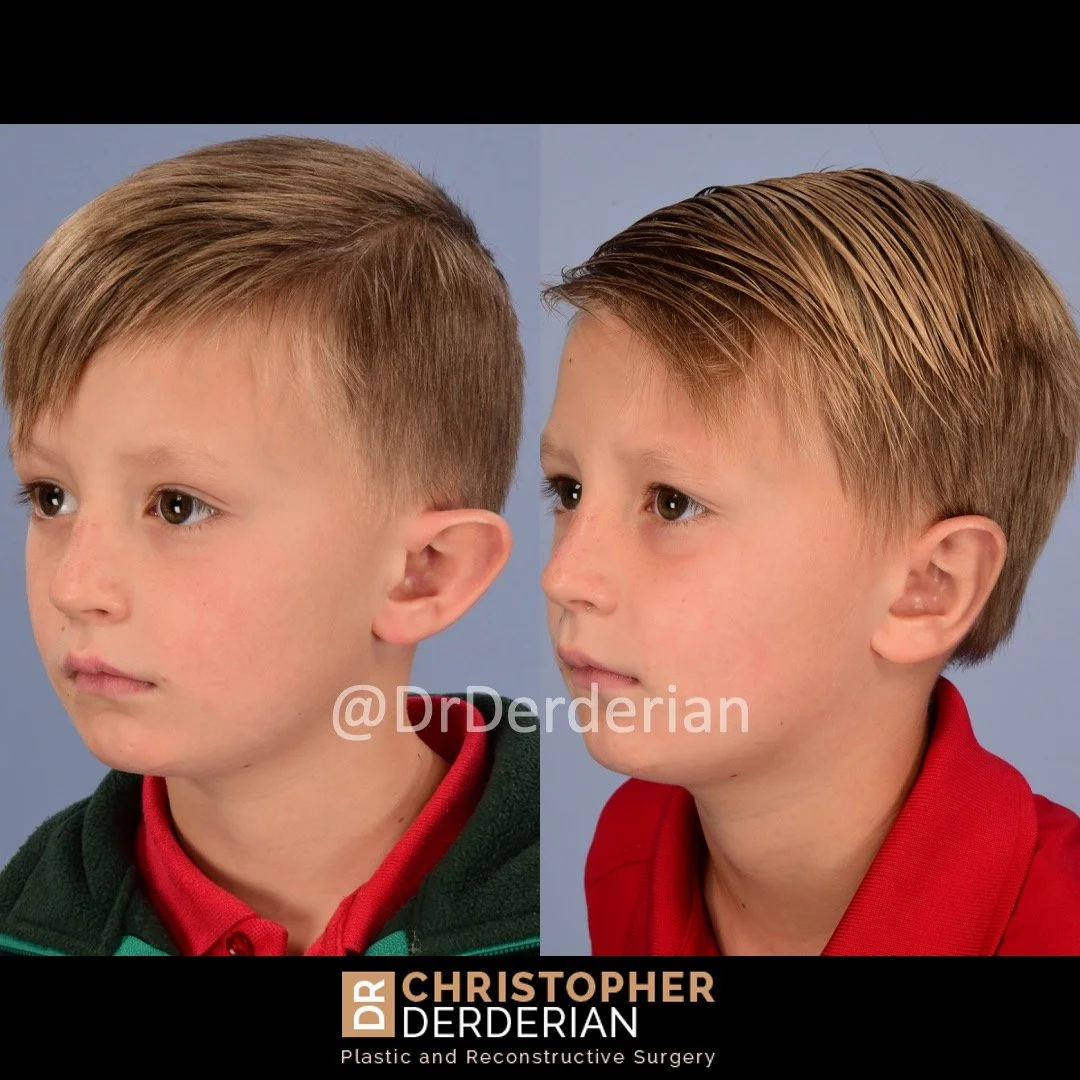
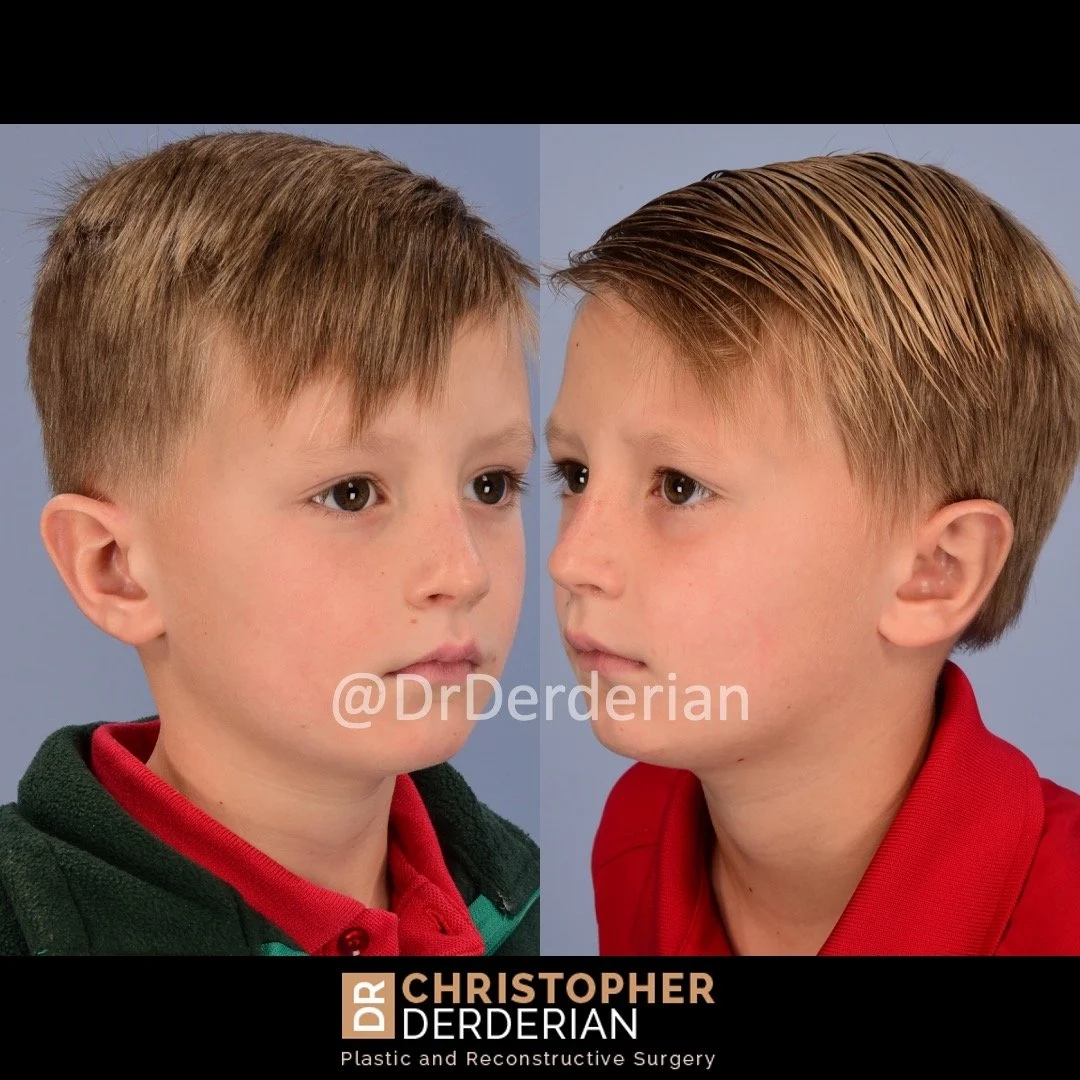
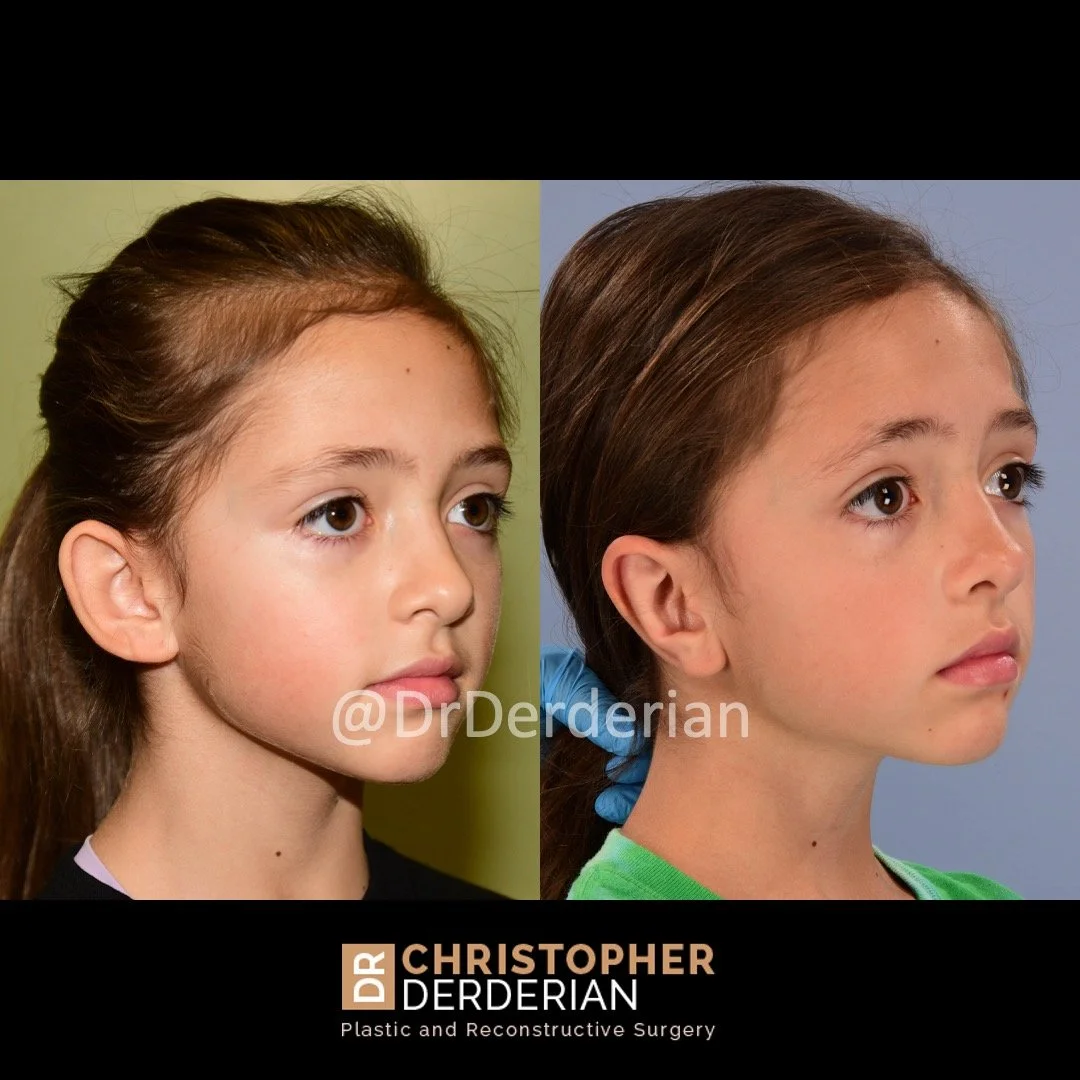
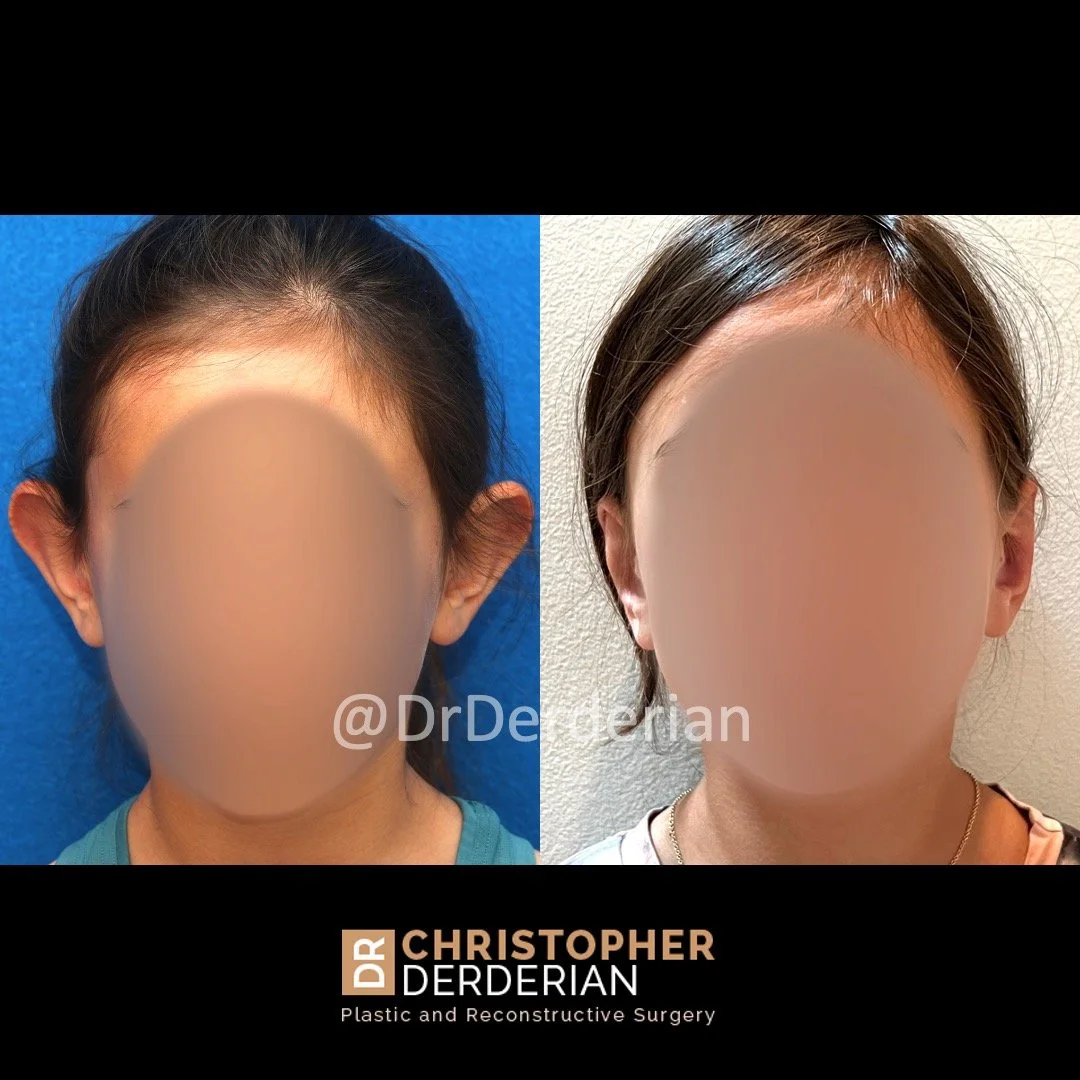
Otoplasty (Ear Surgery)
in Dallas,
Texas
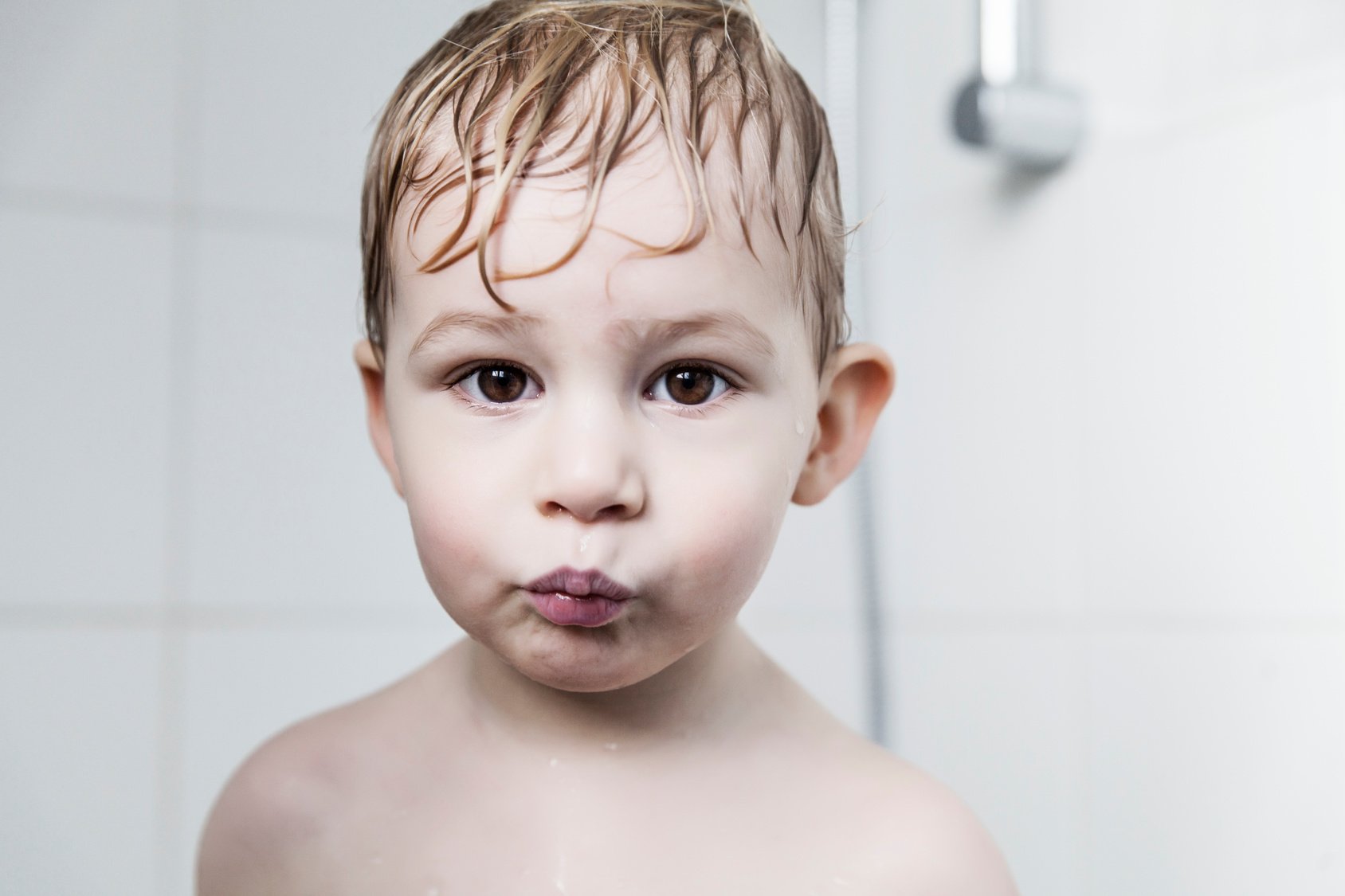
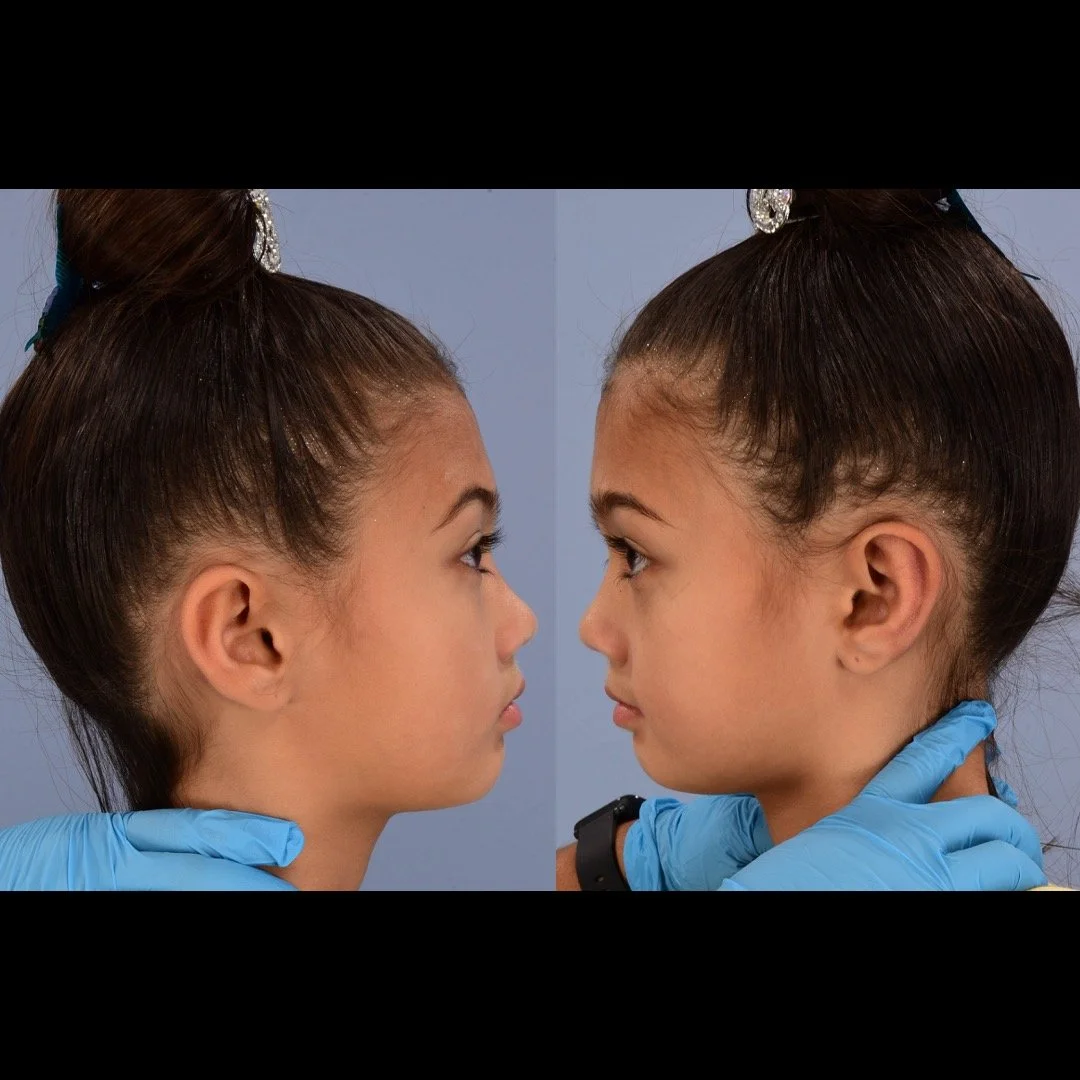
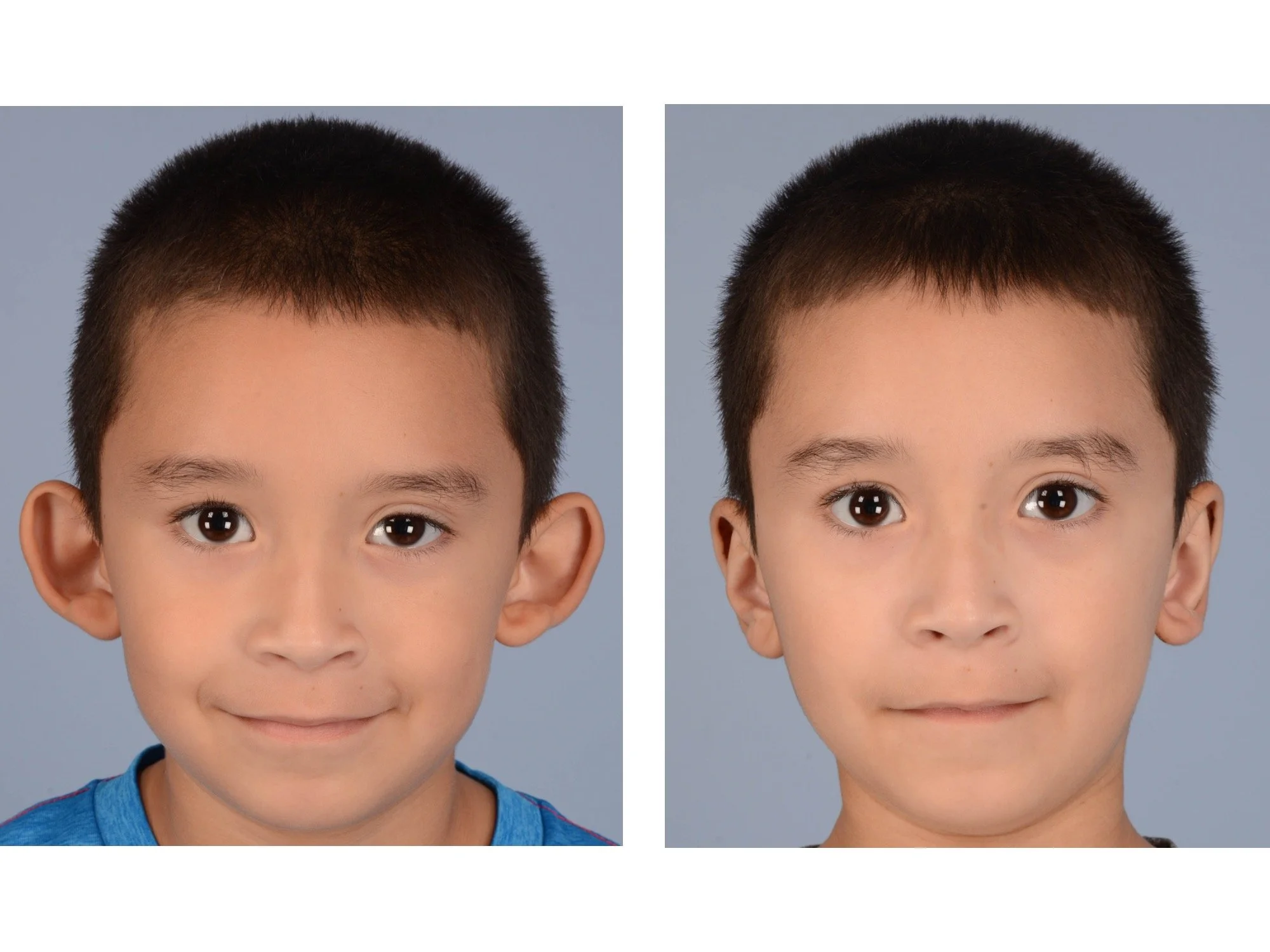
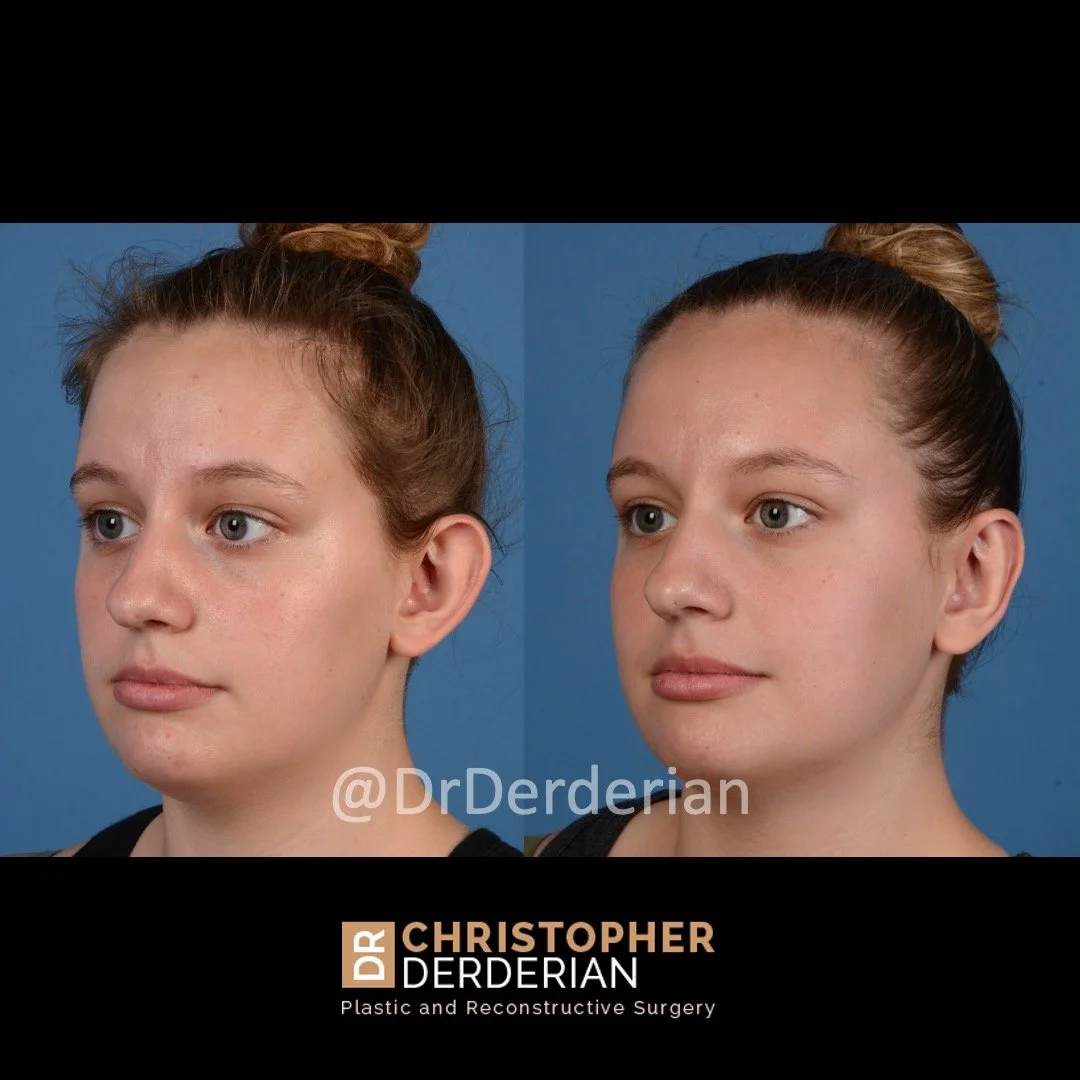
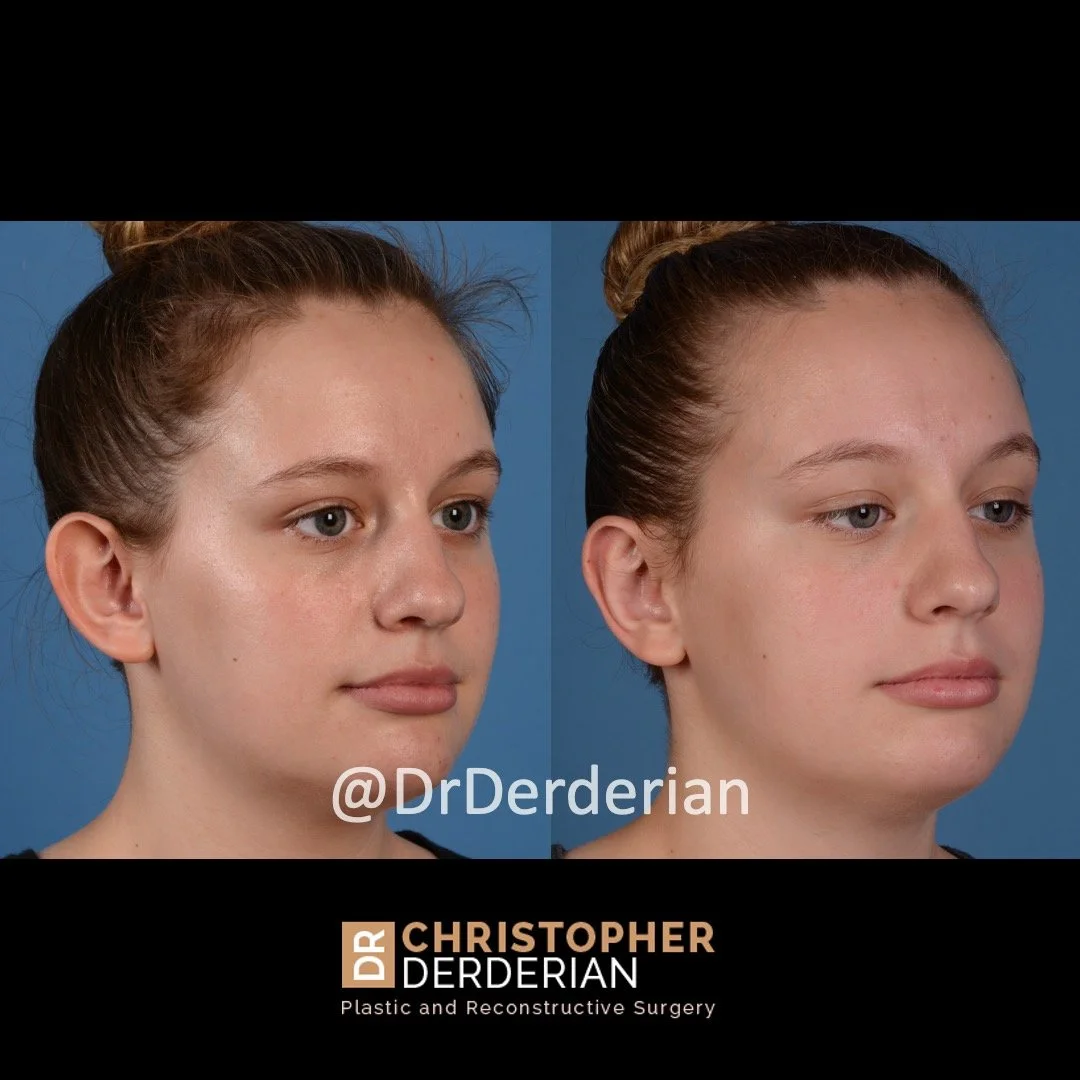
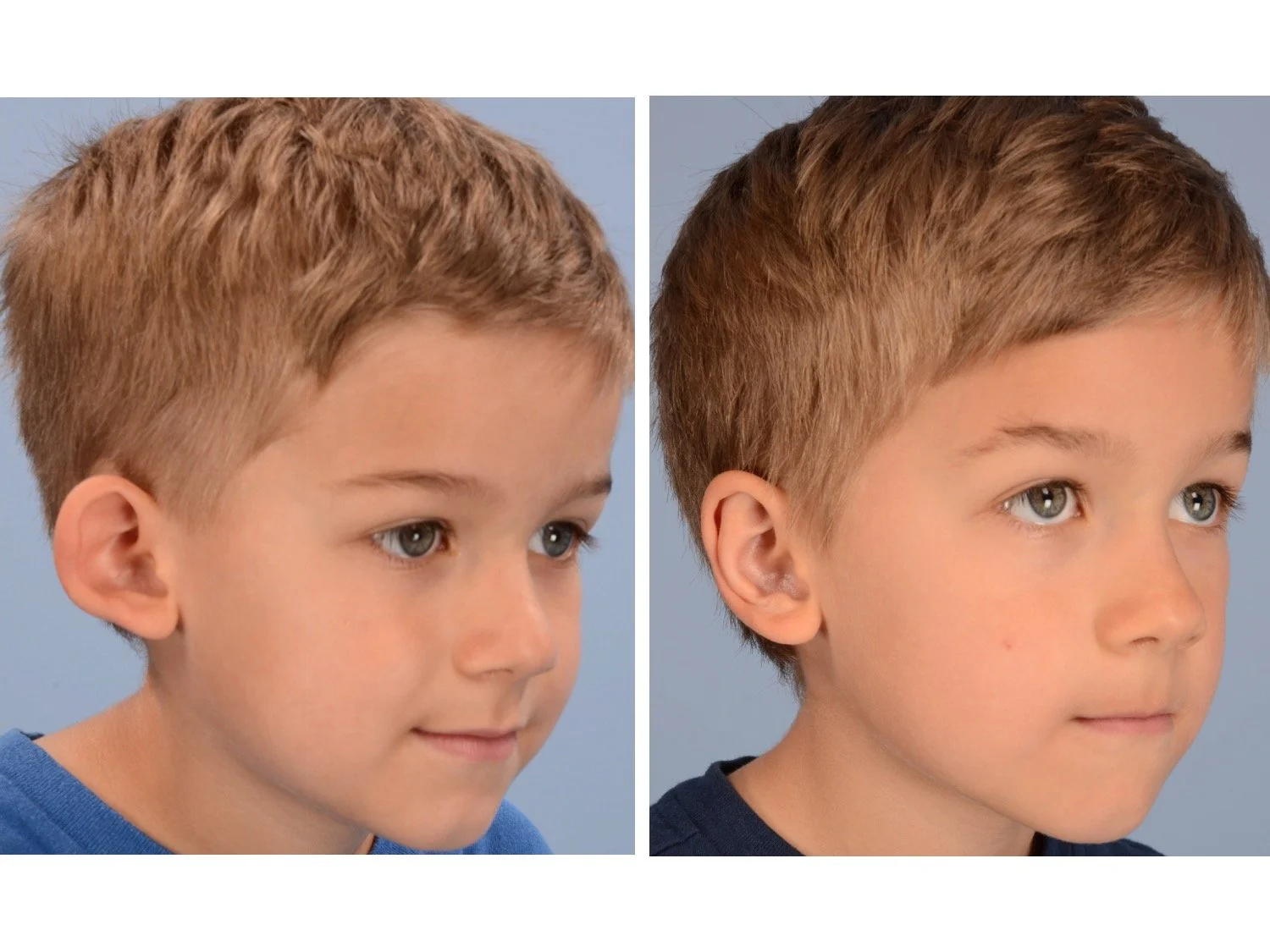
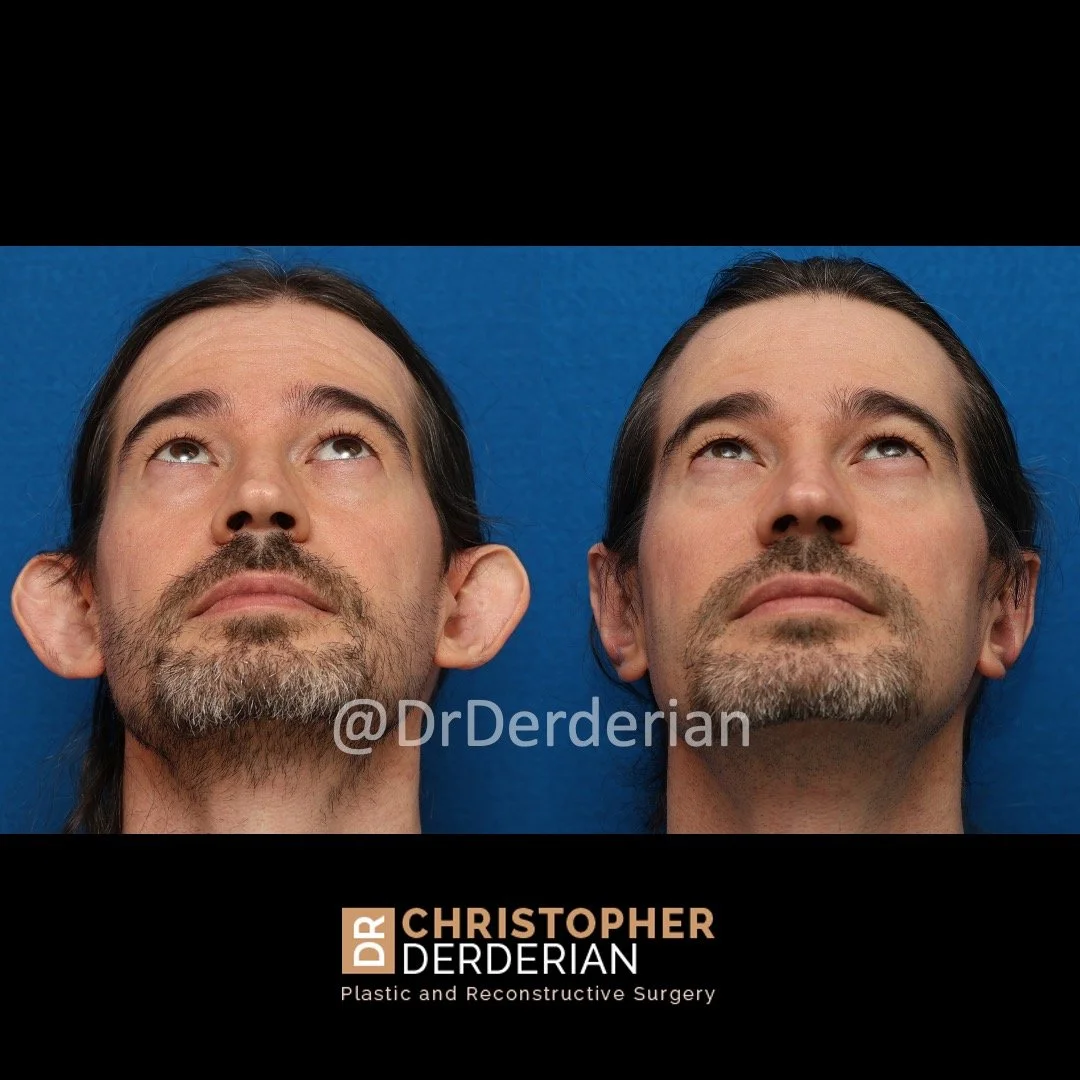
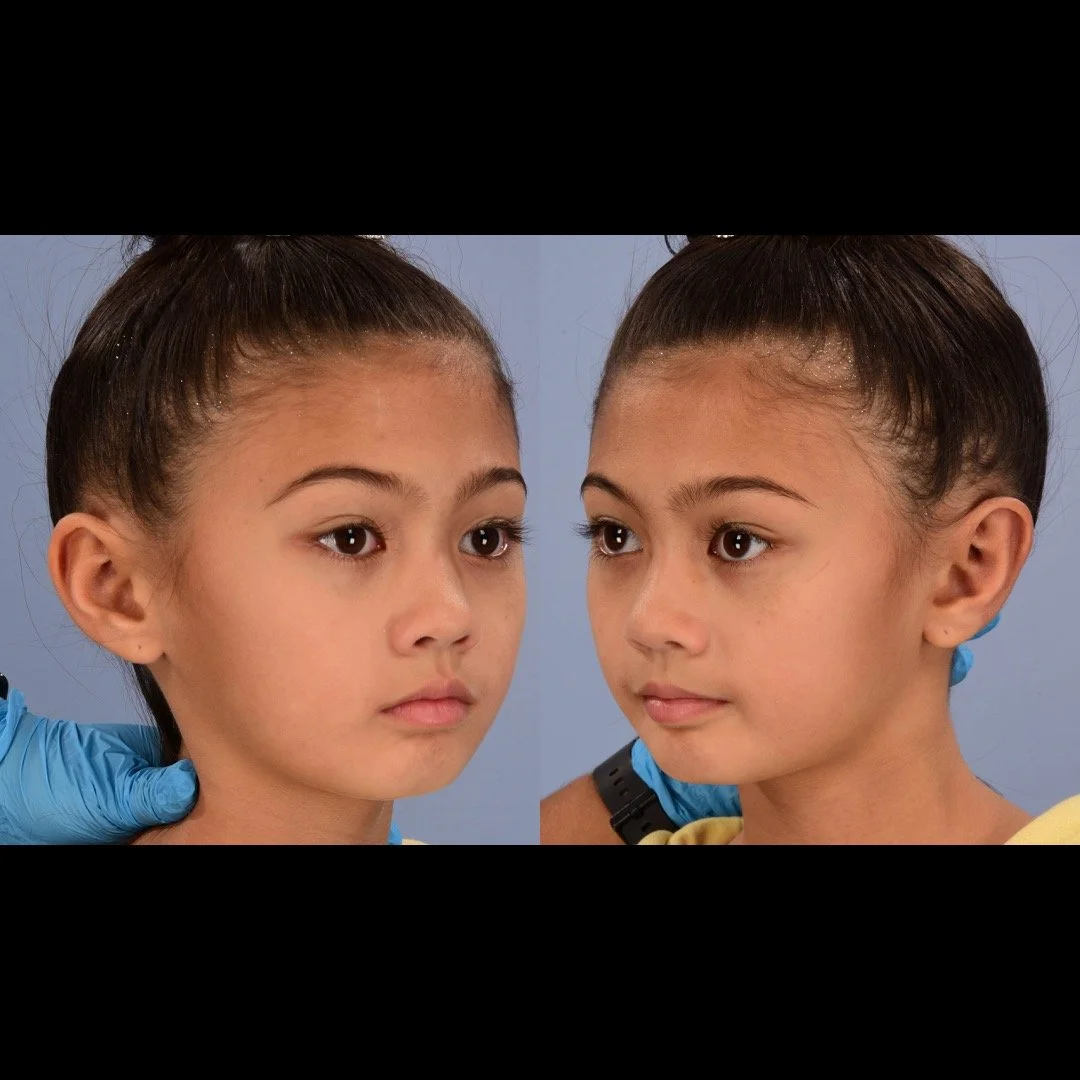
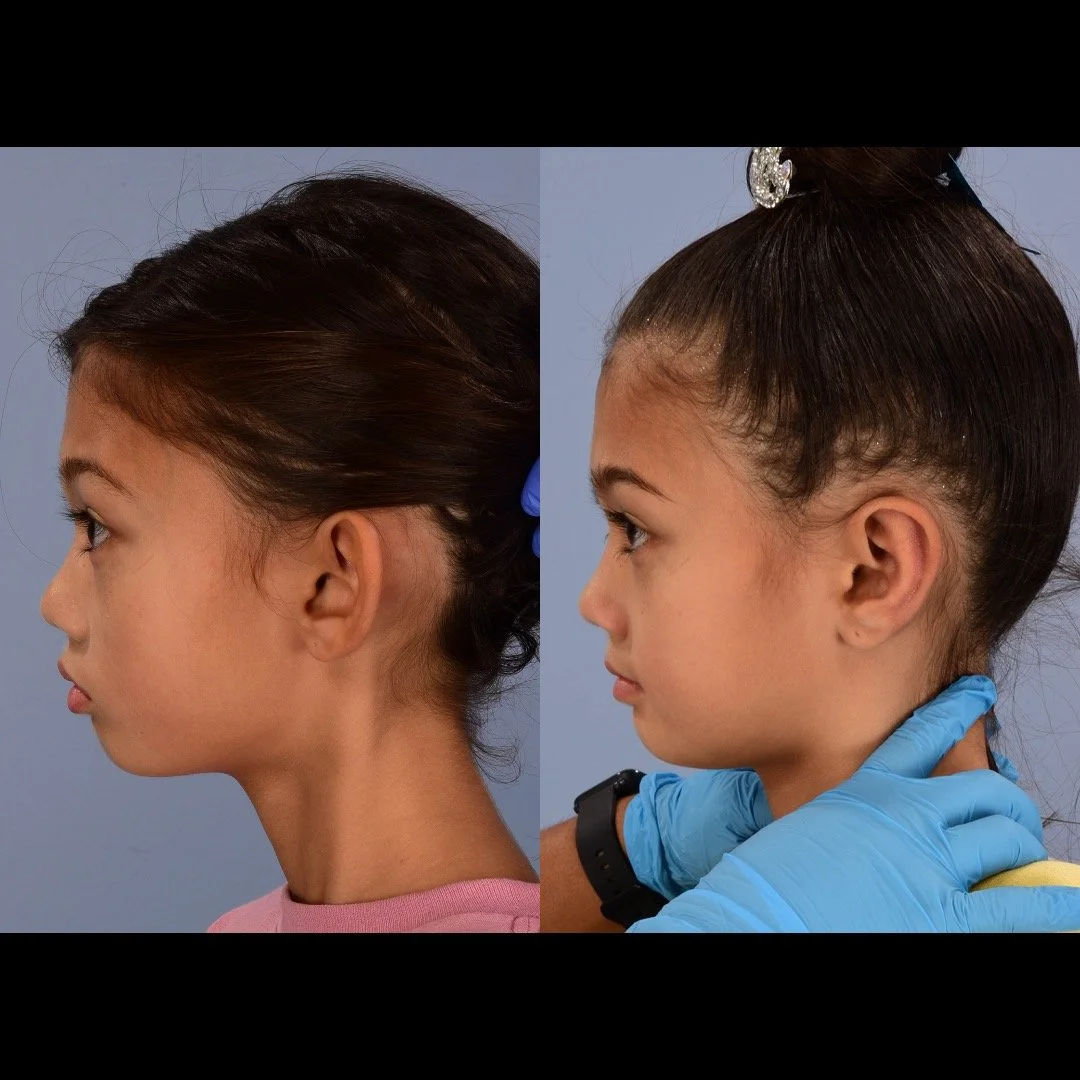
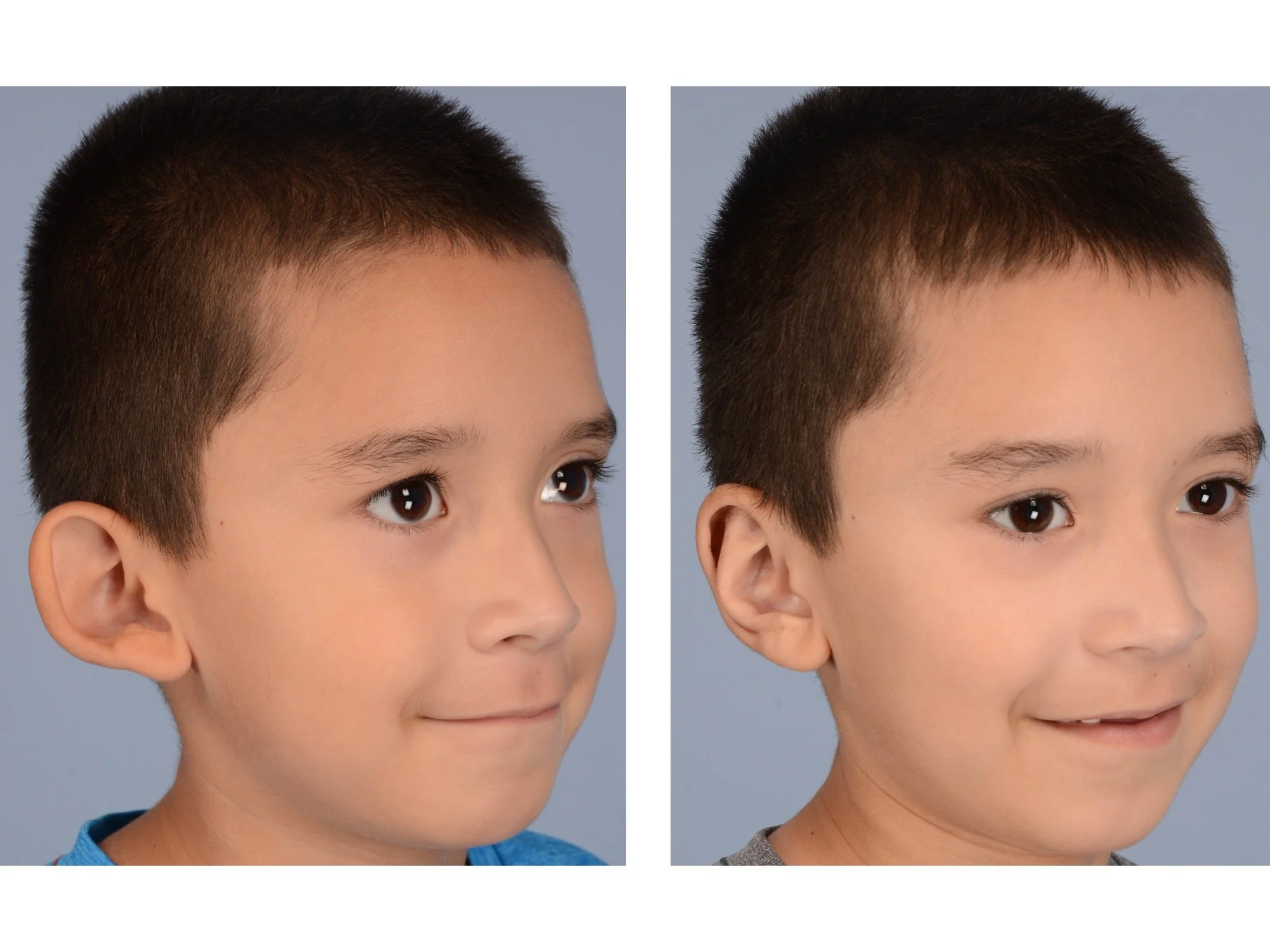
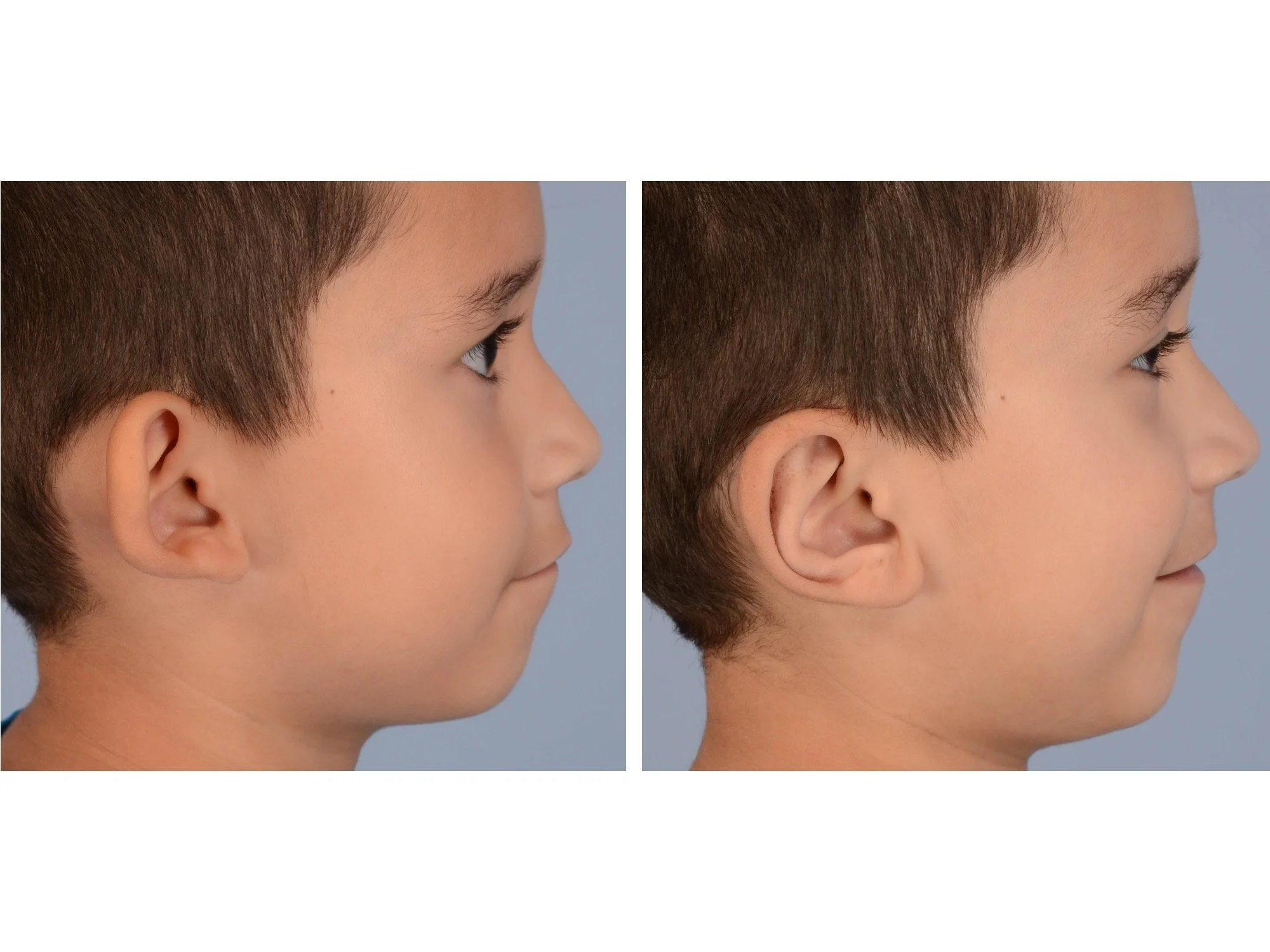
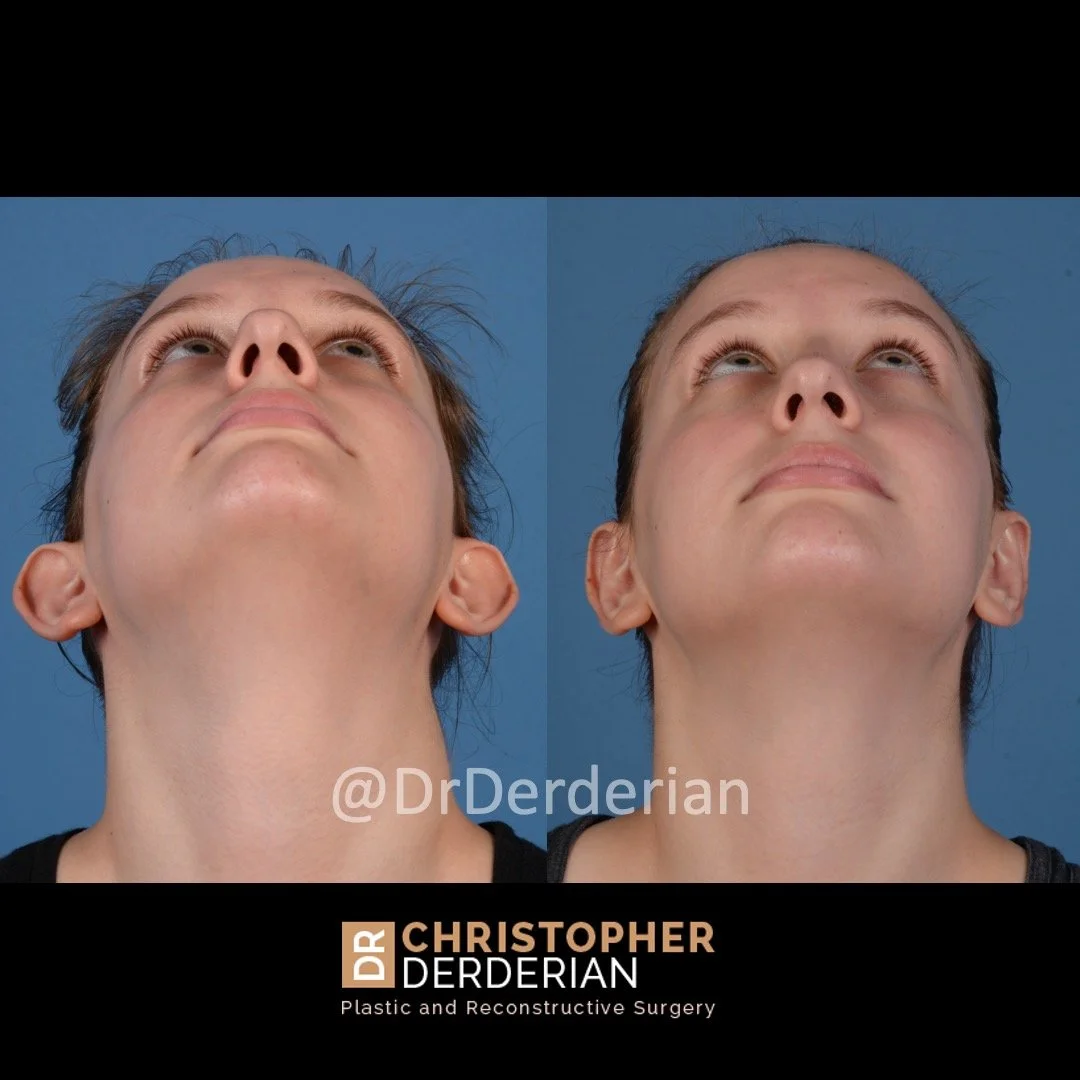
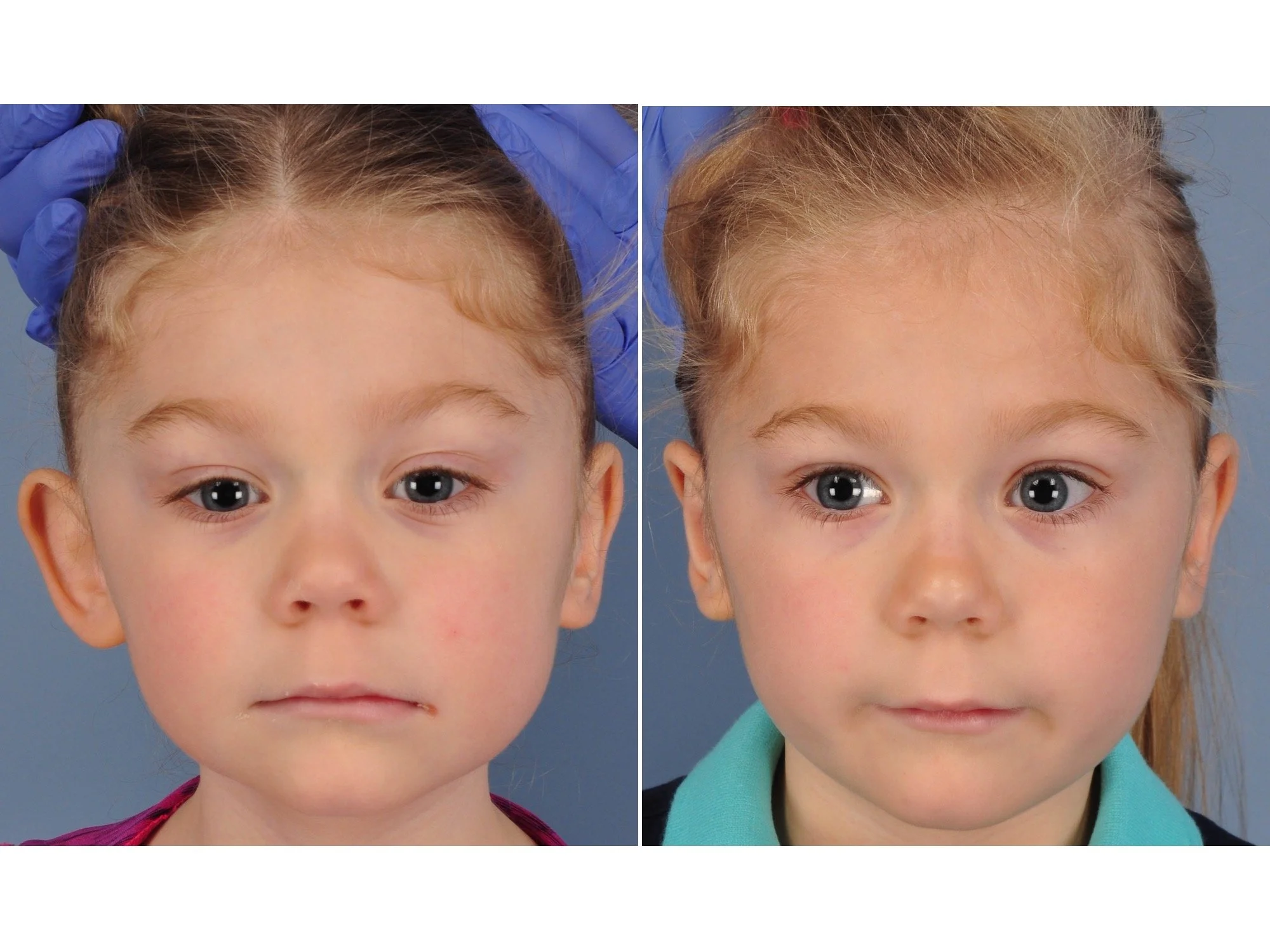
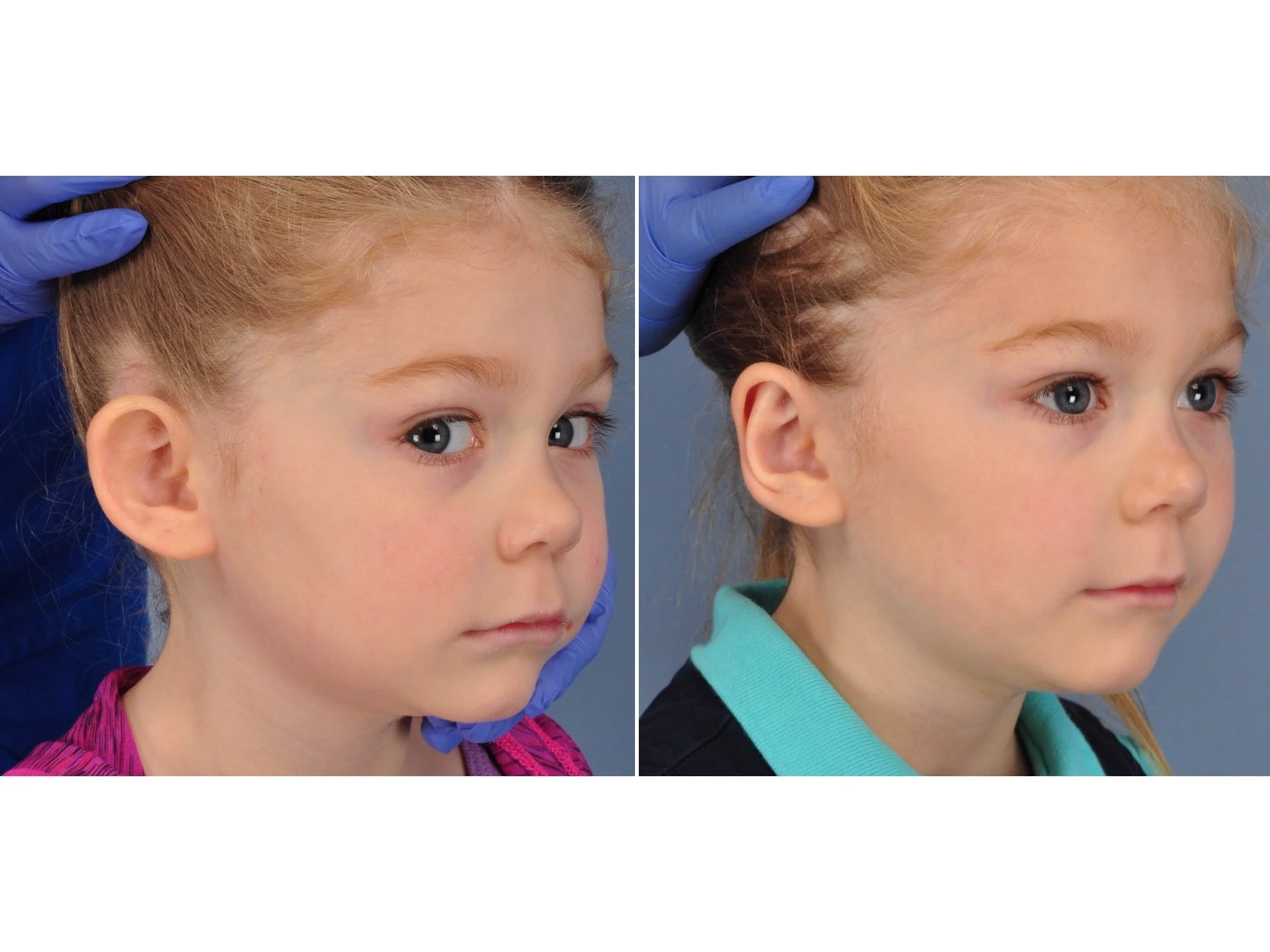
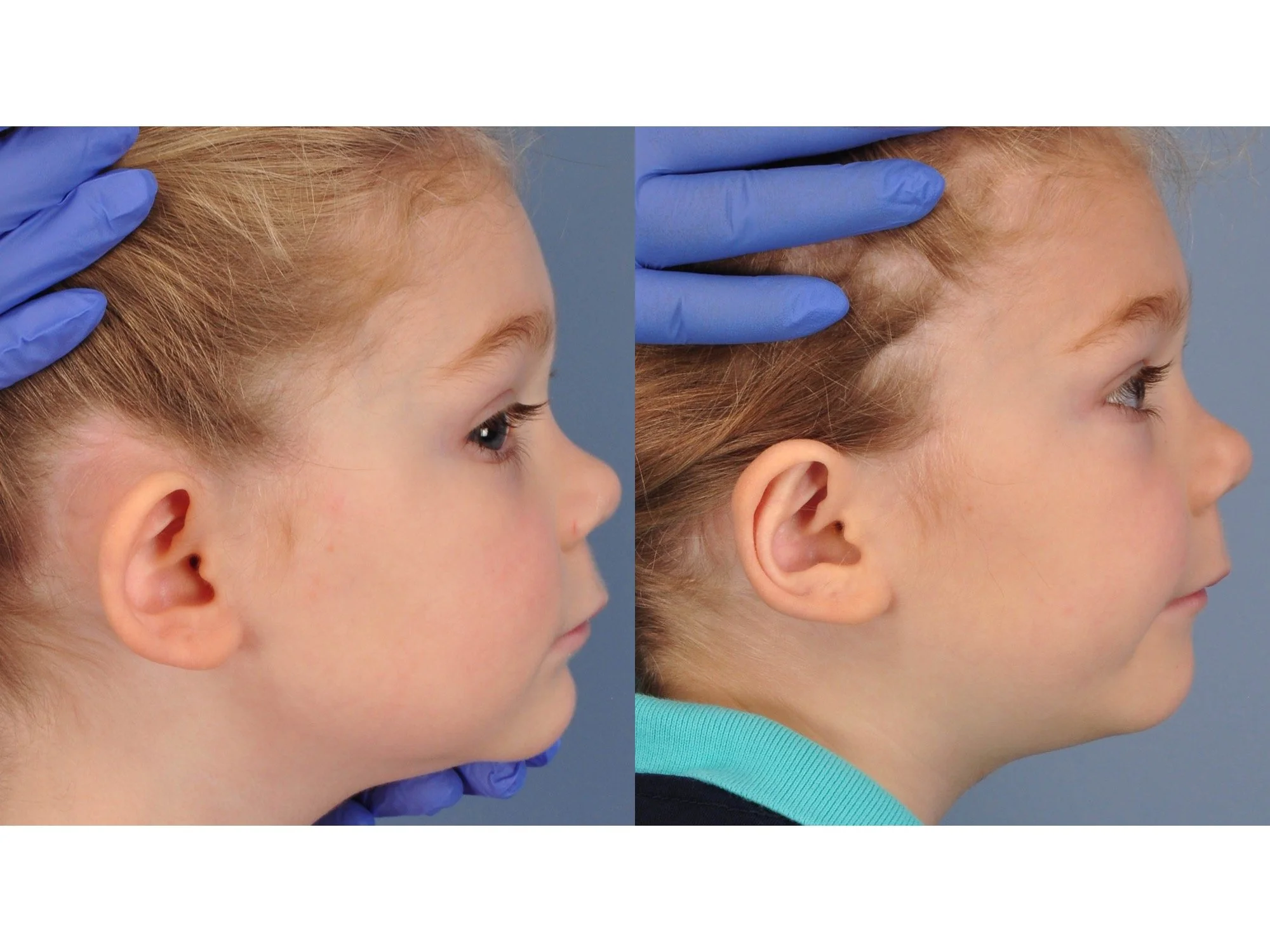
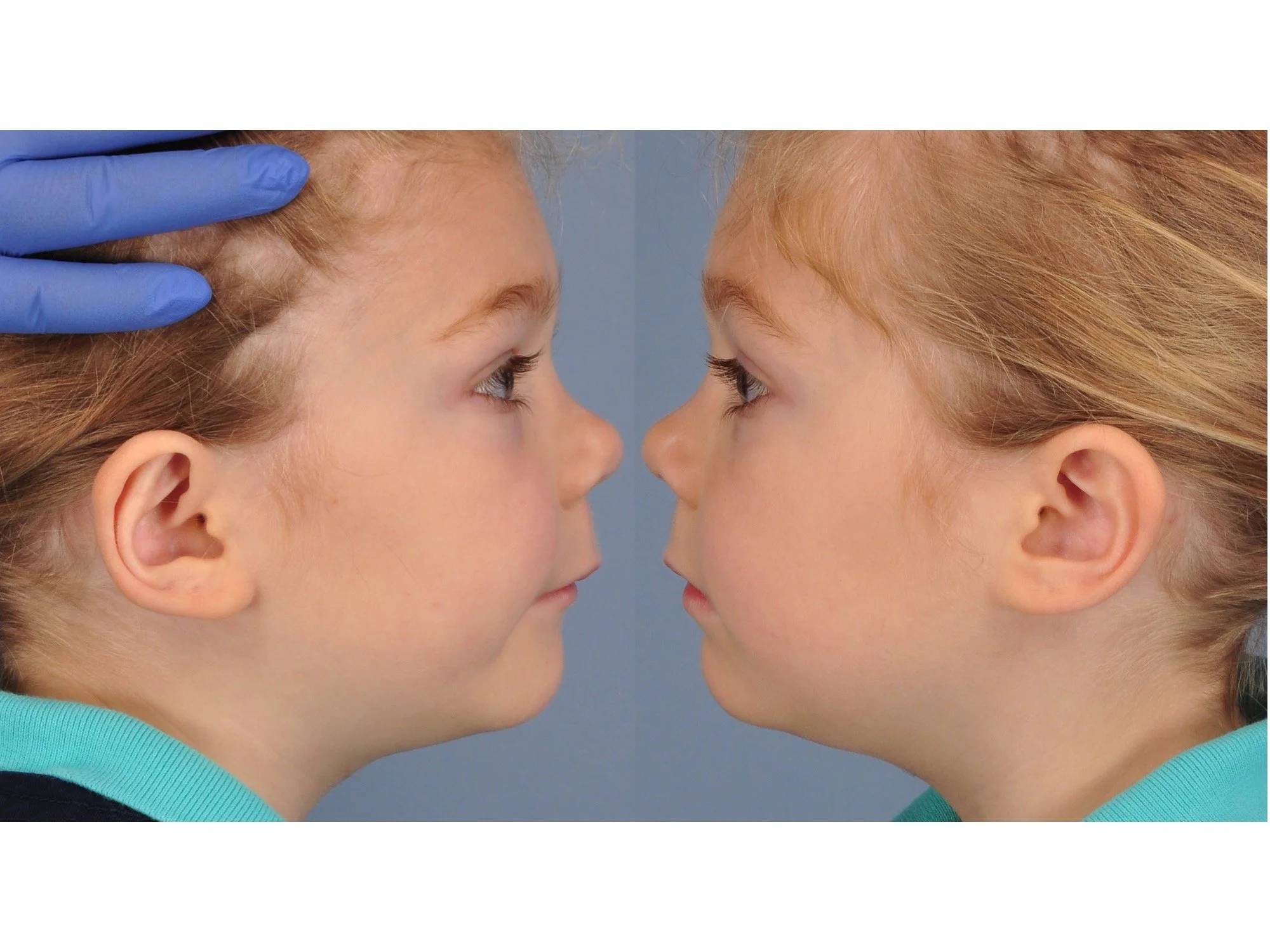
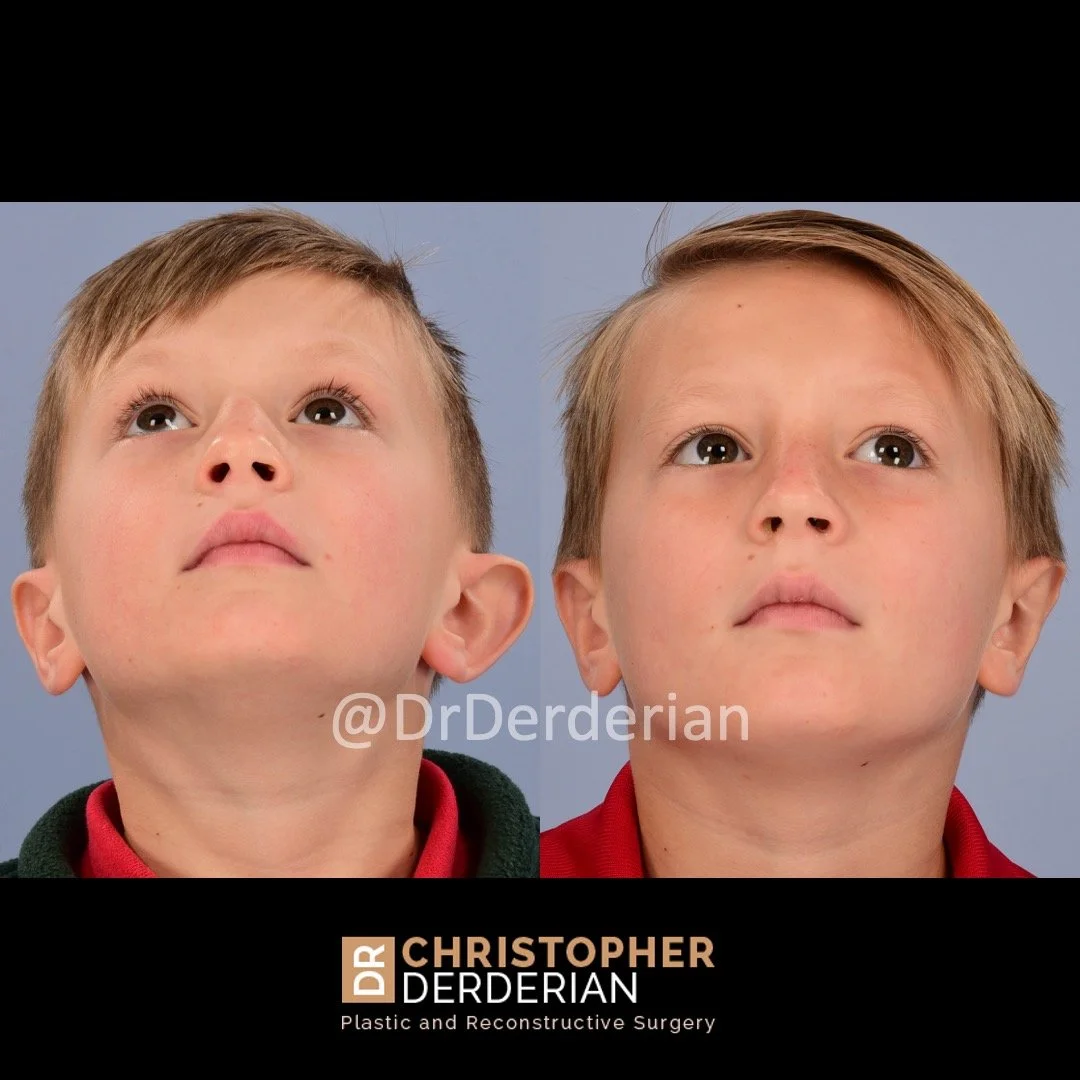
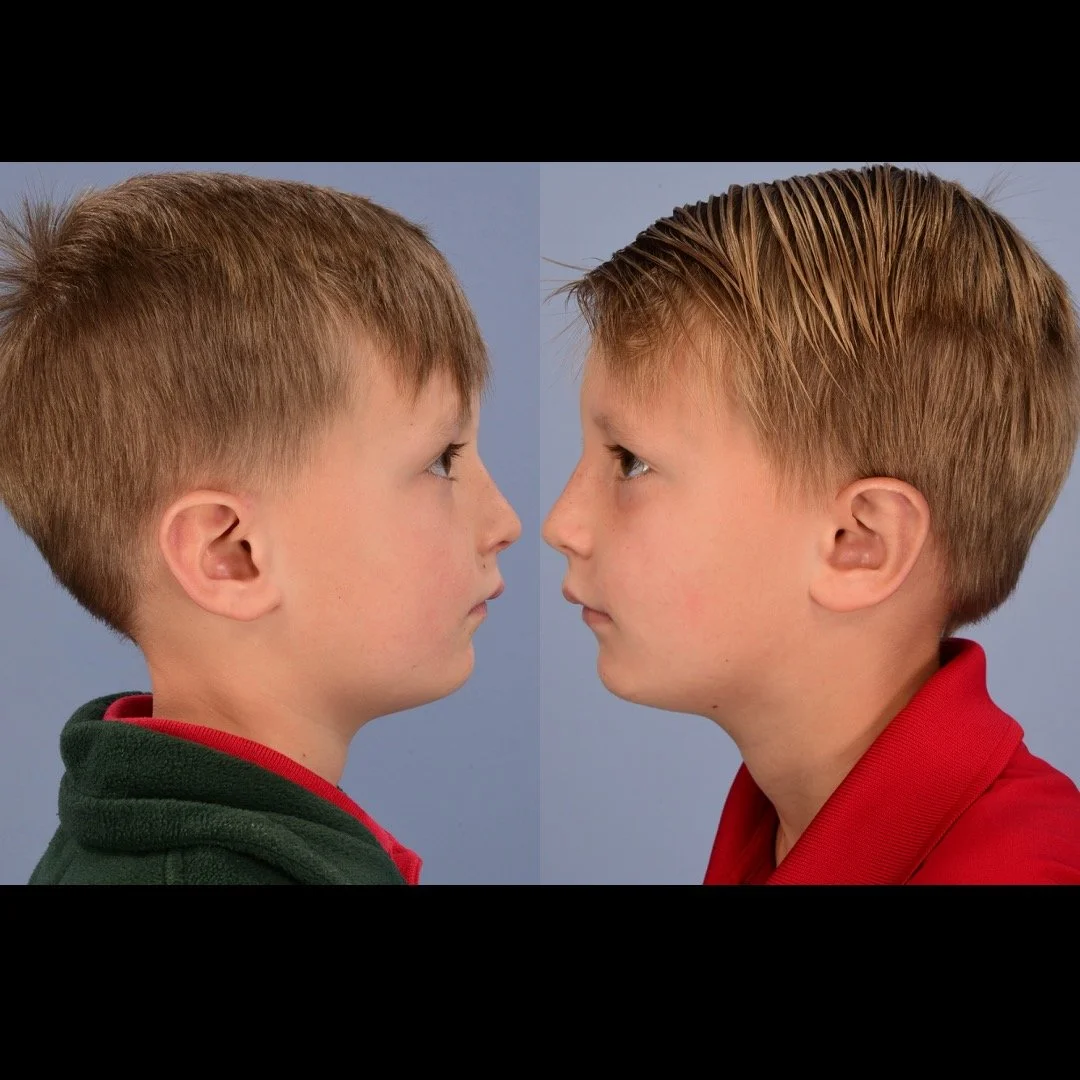
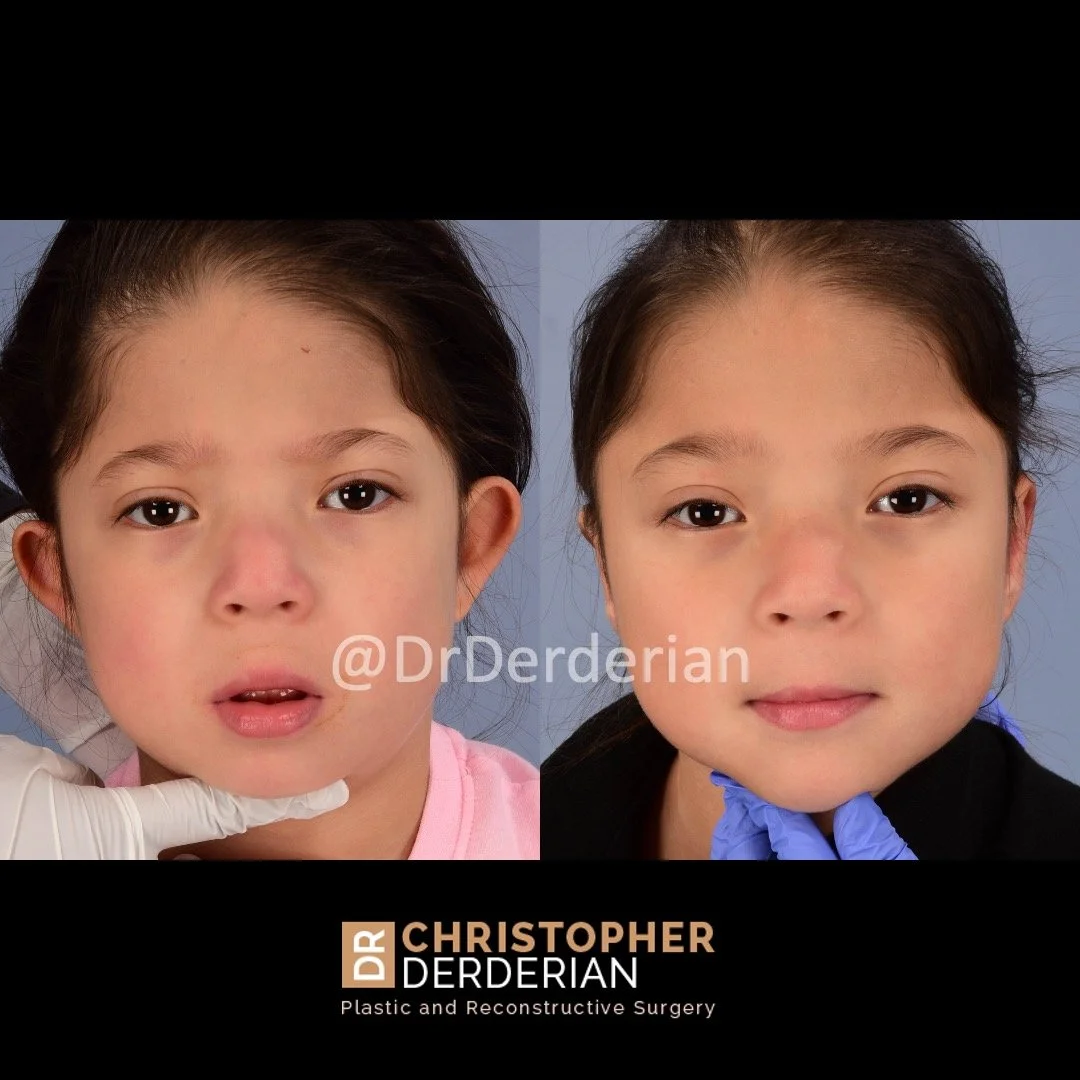
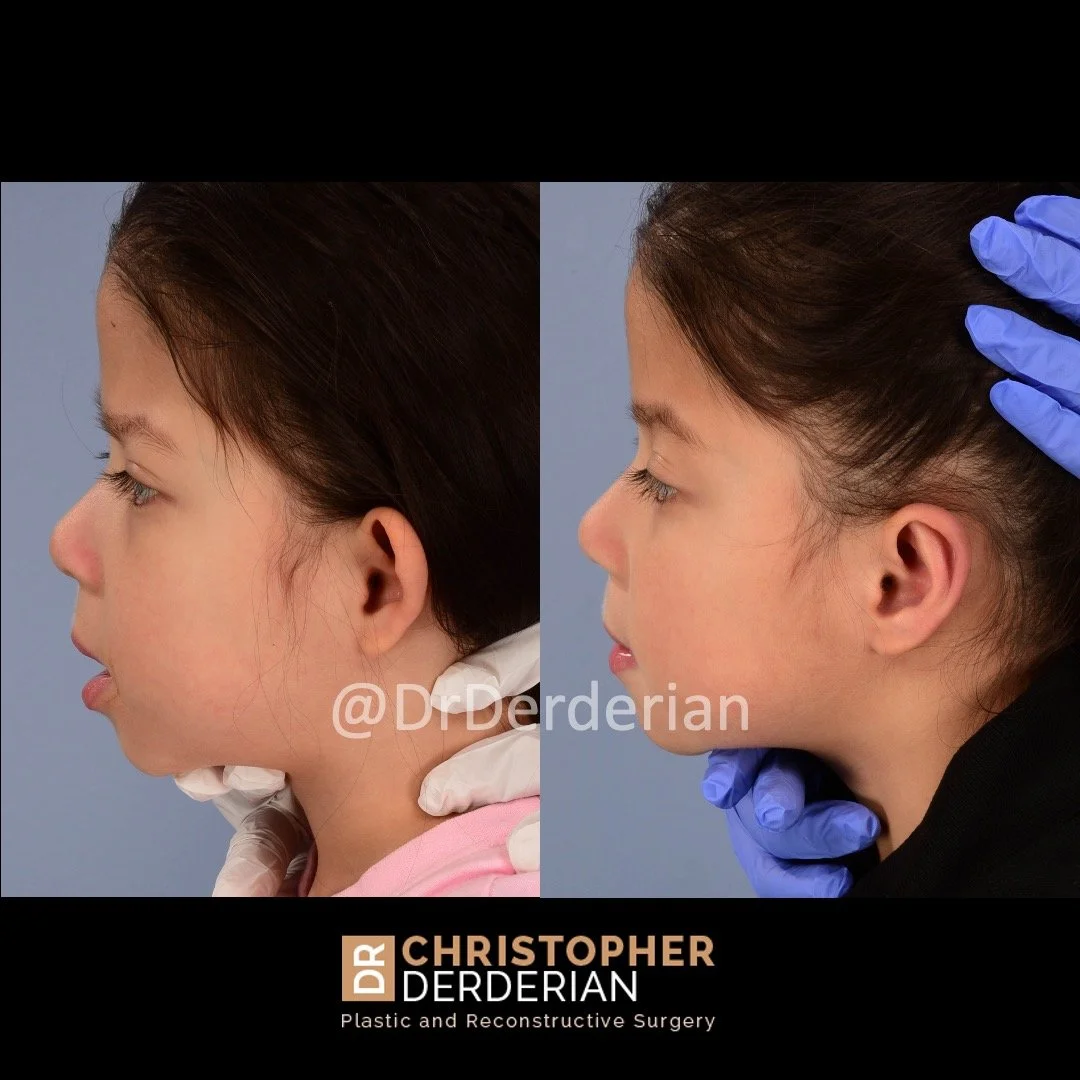
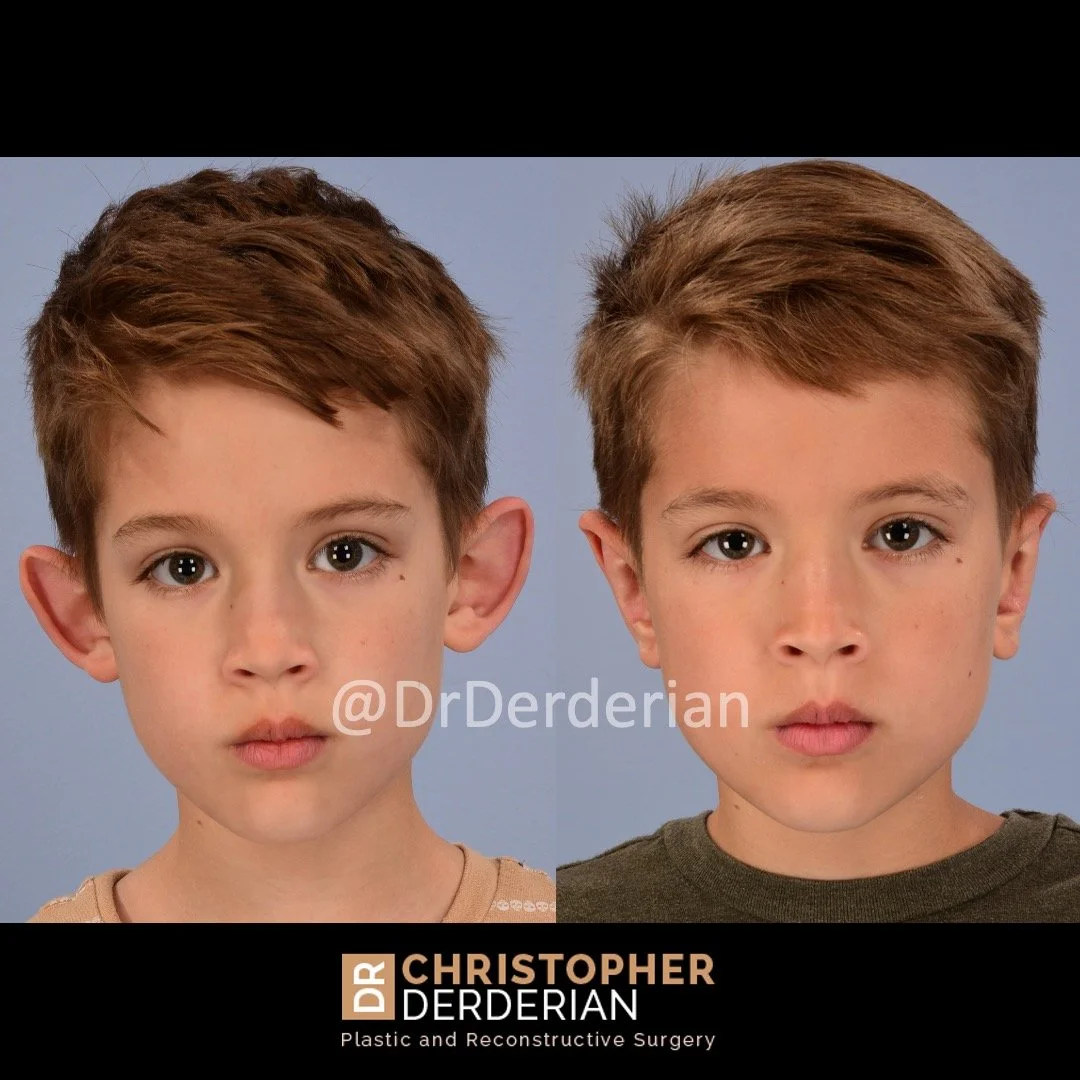
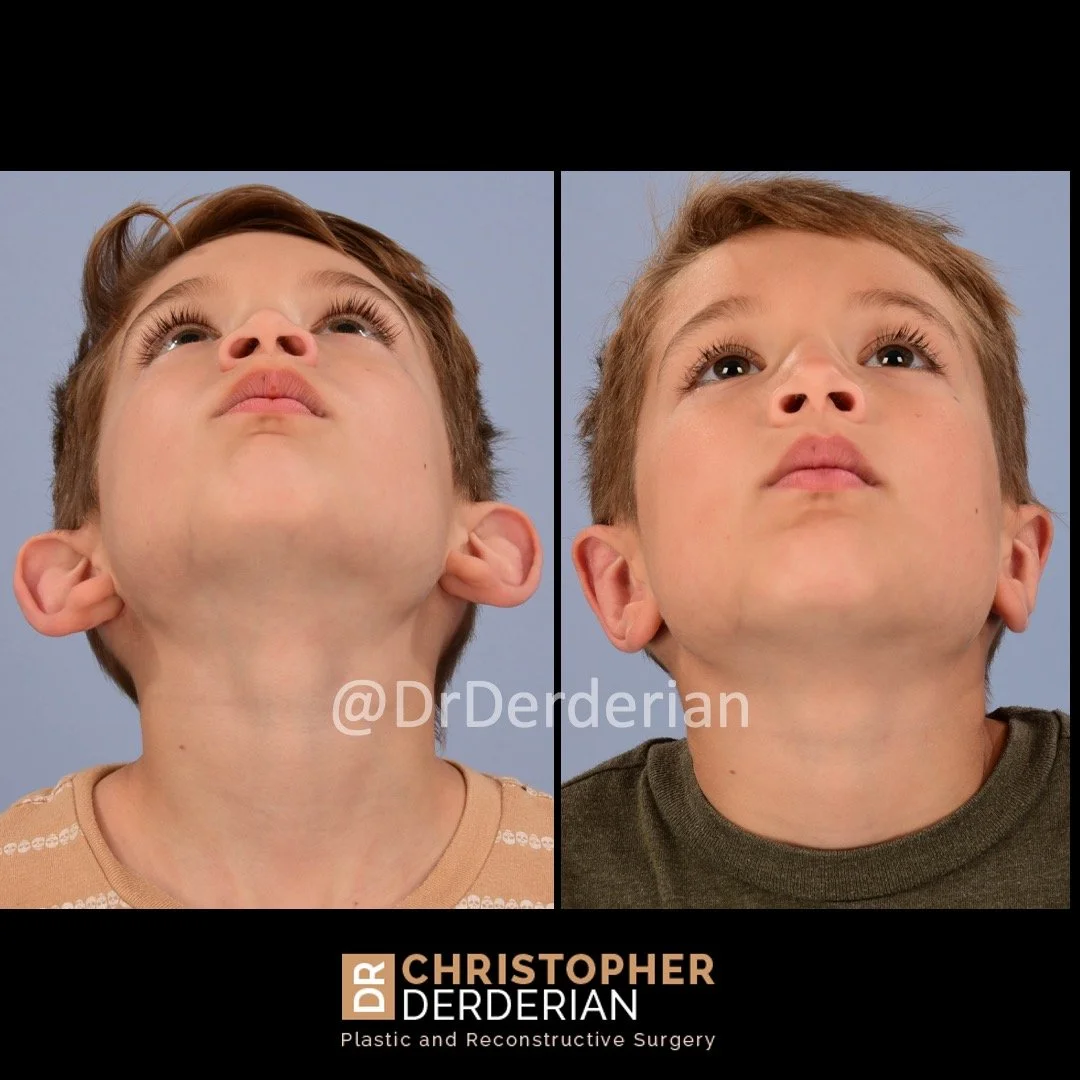
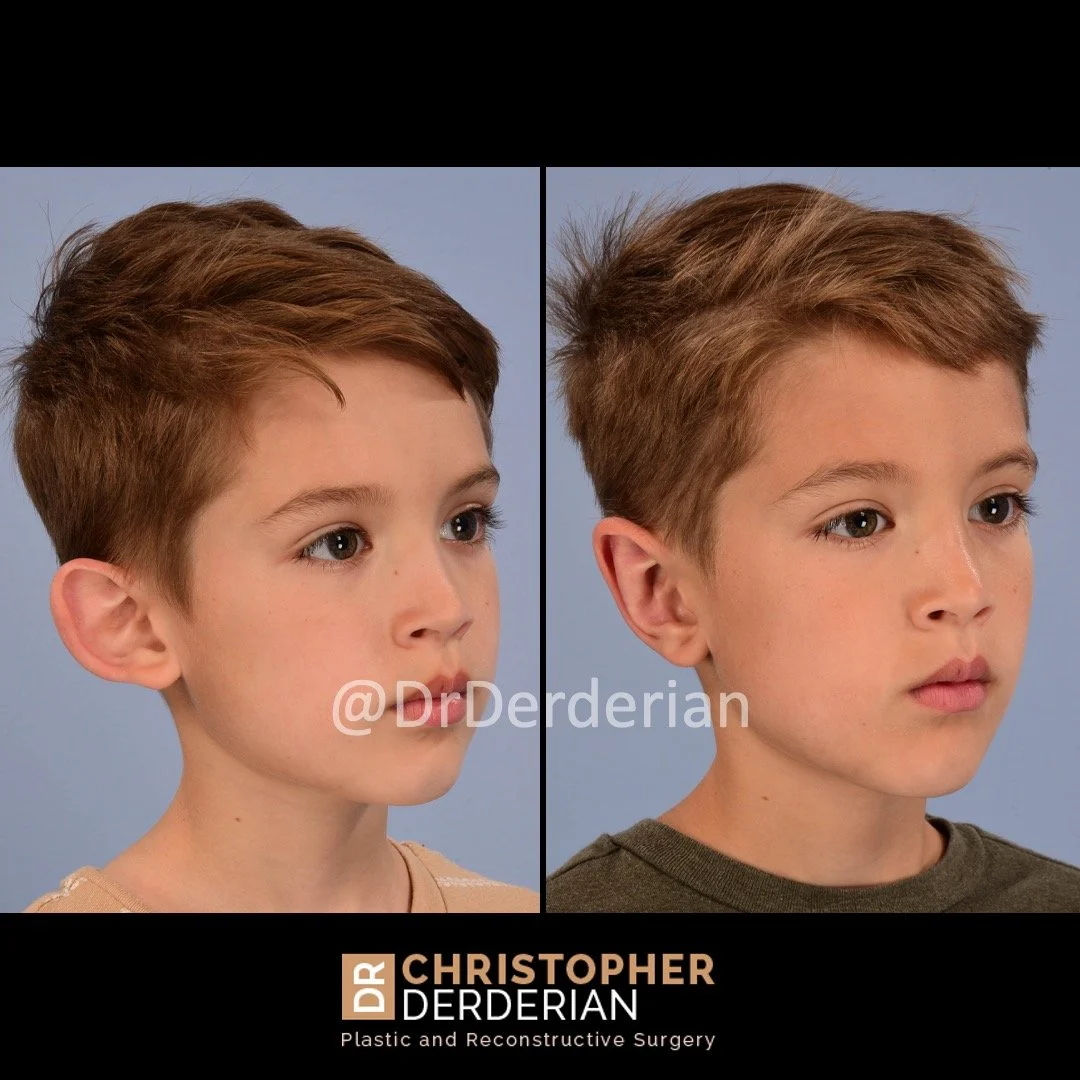
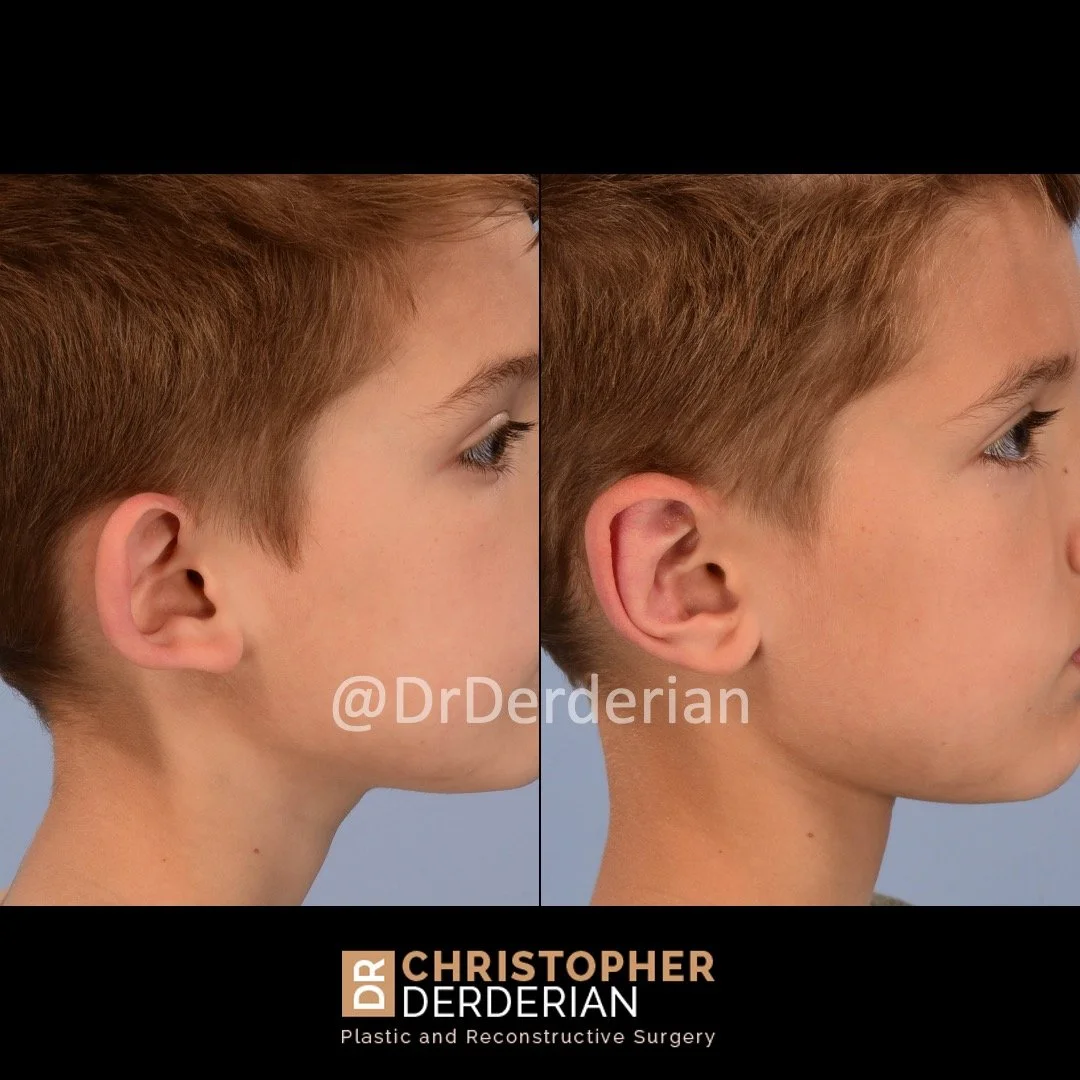
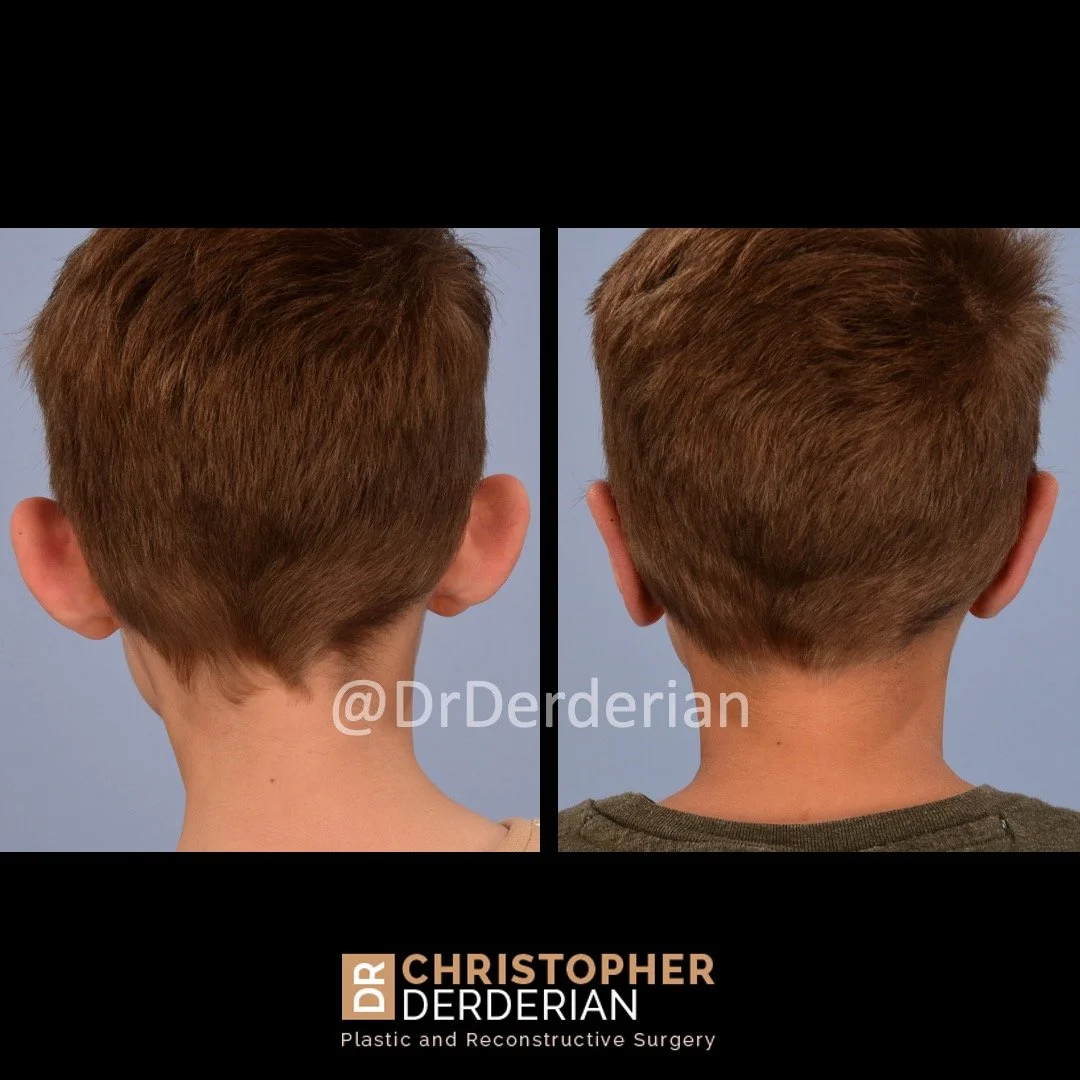
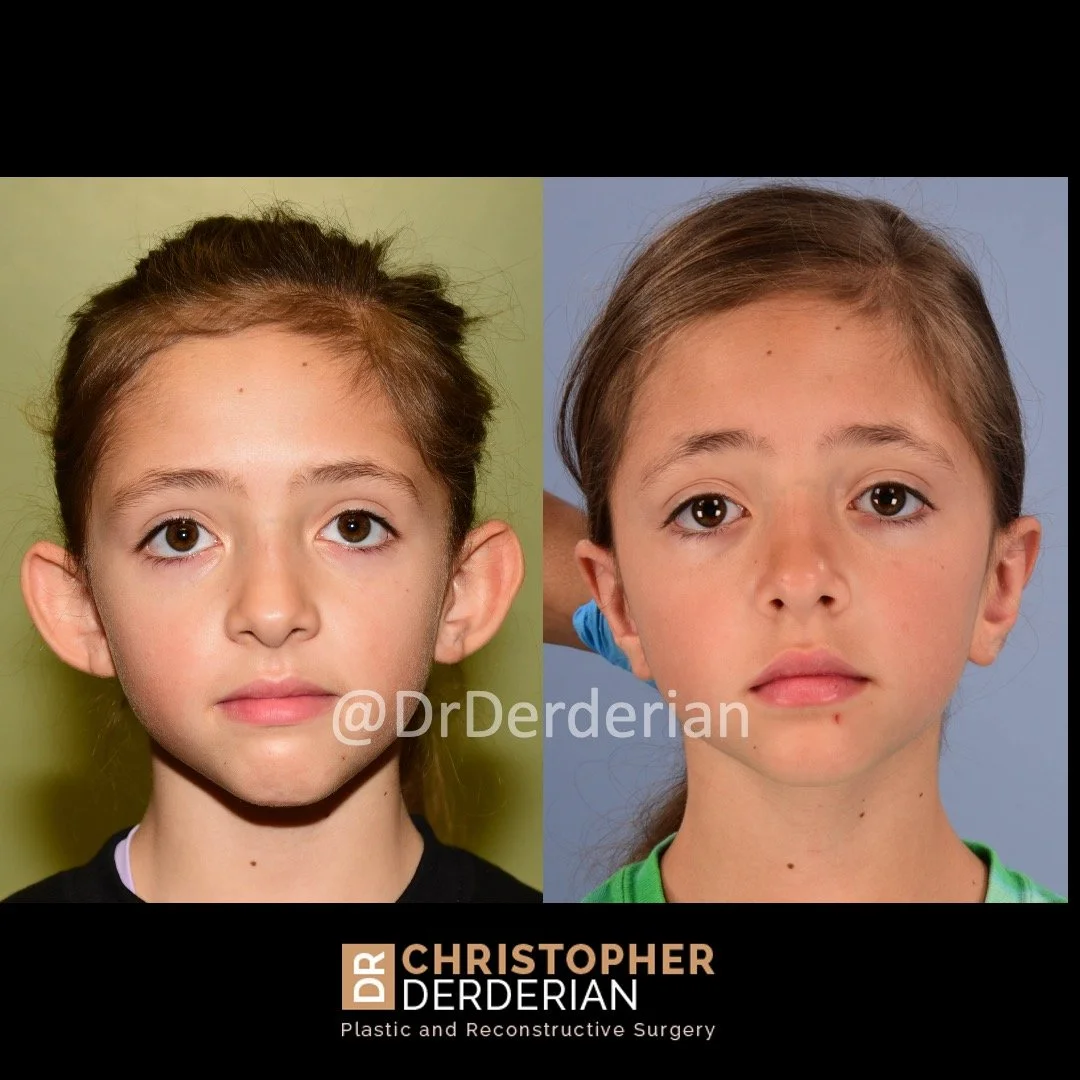
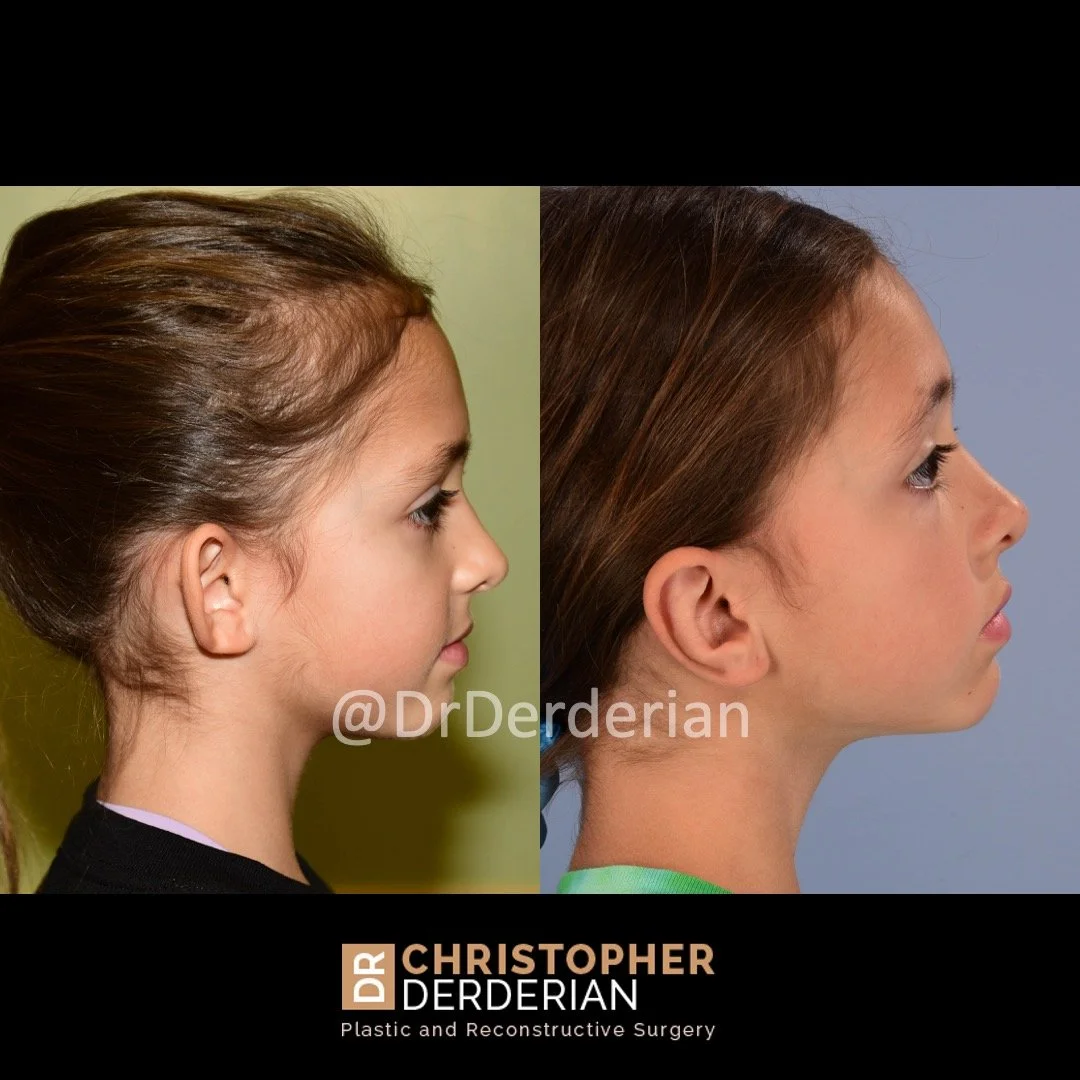
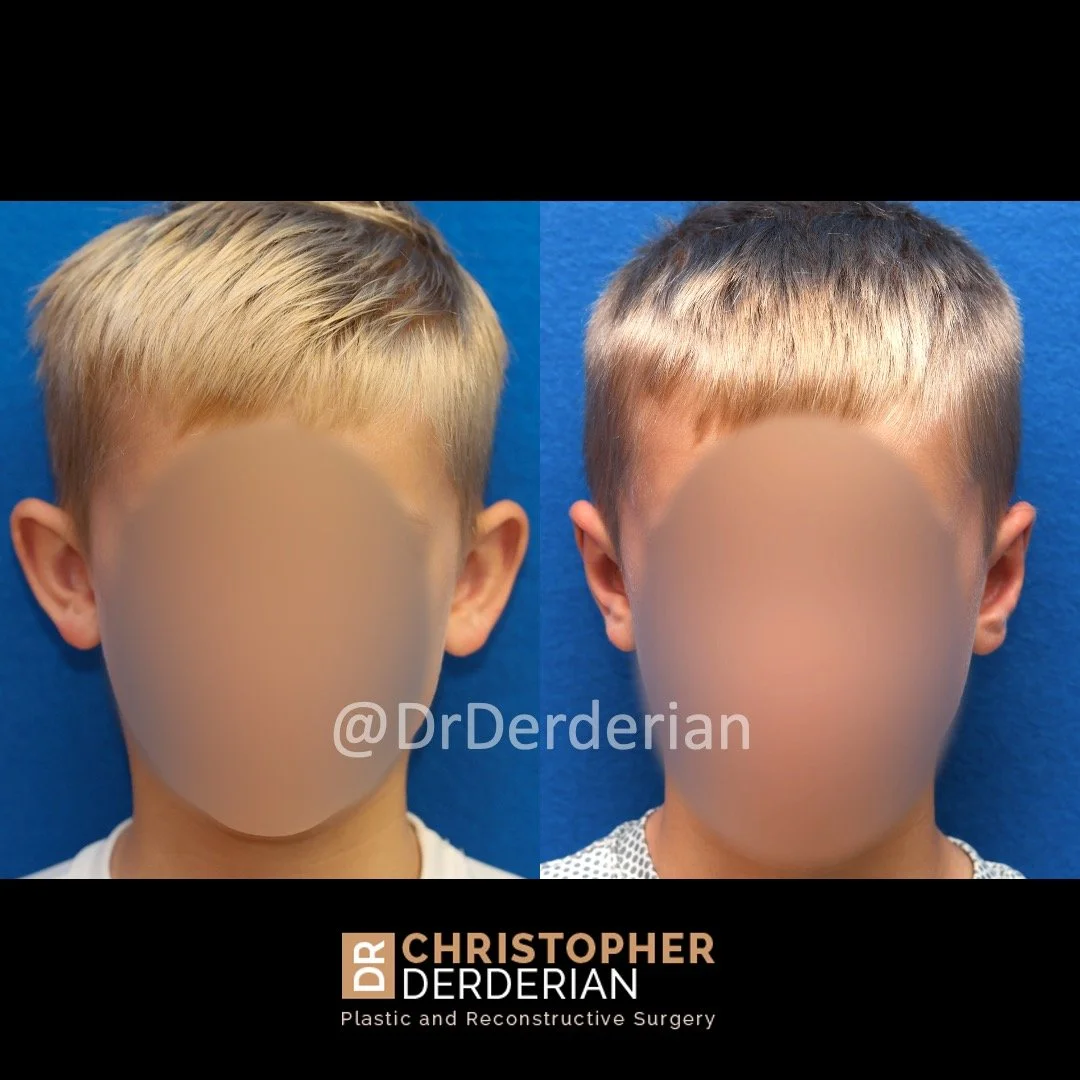
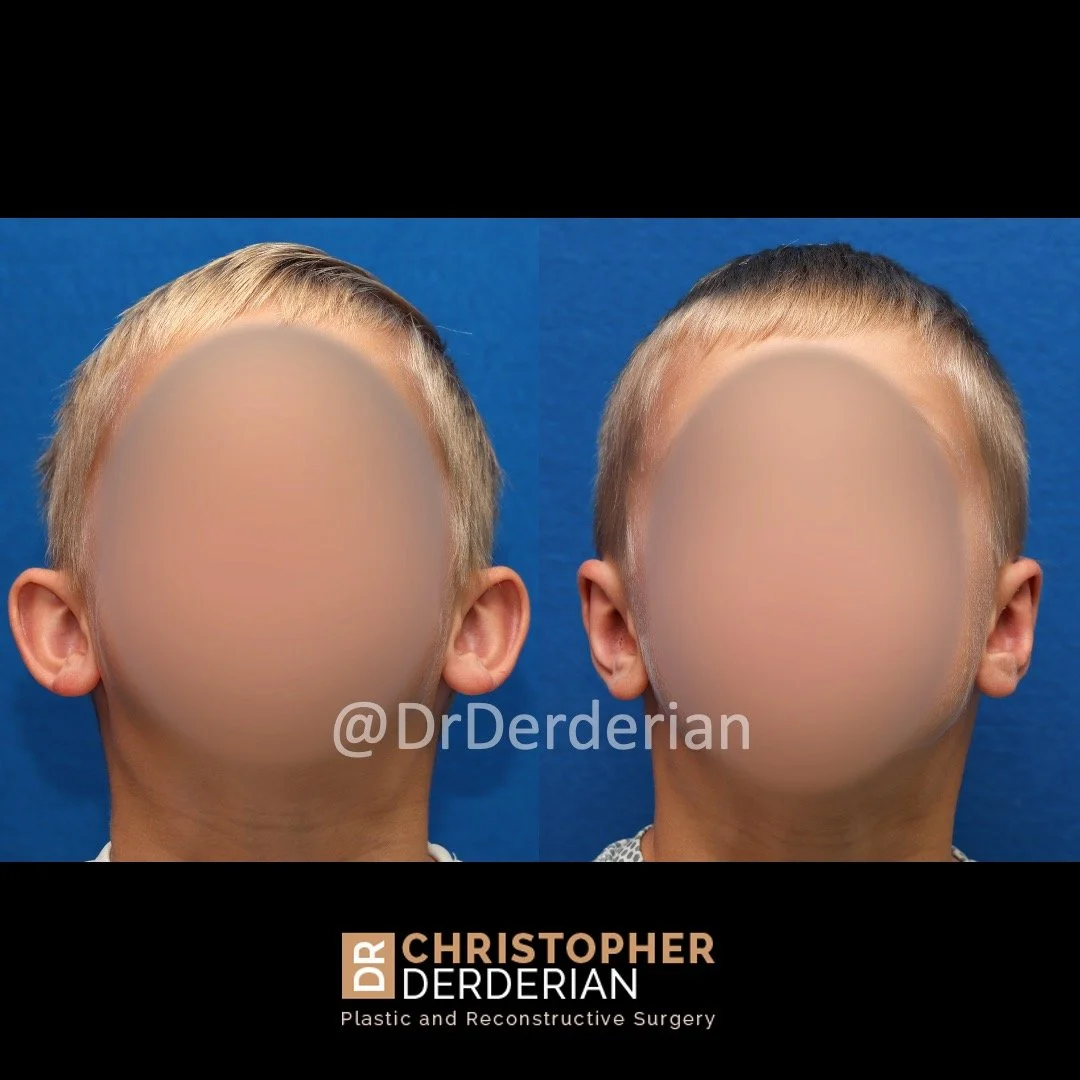
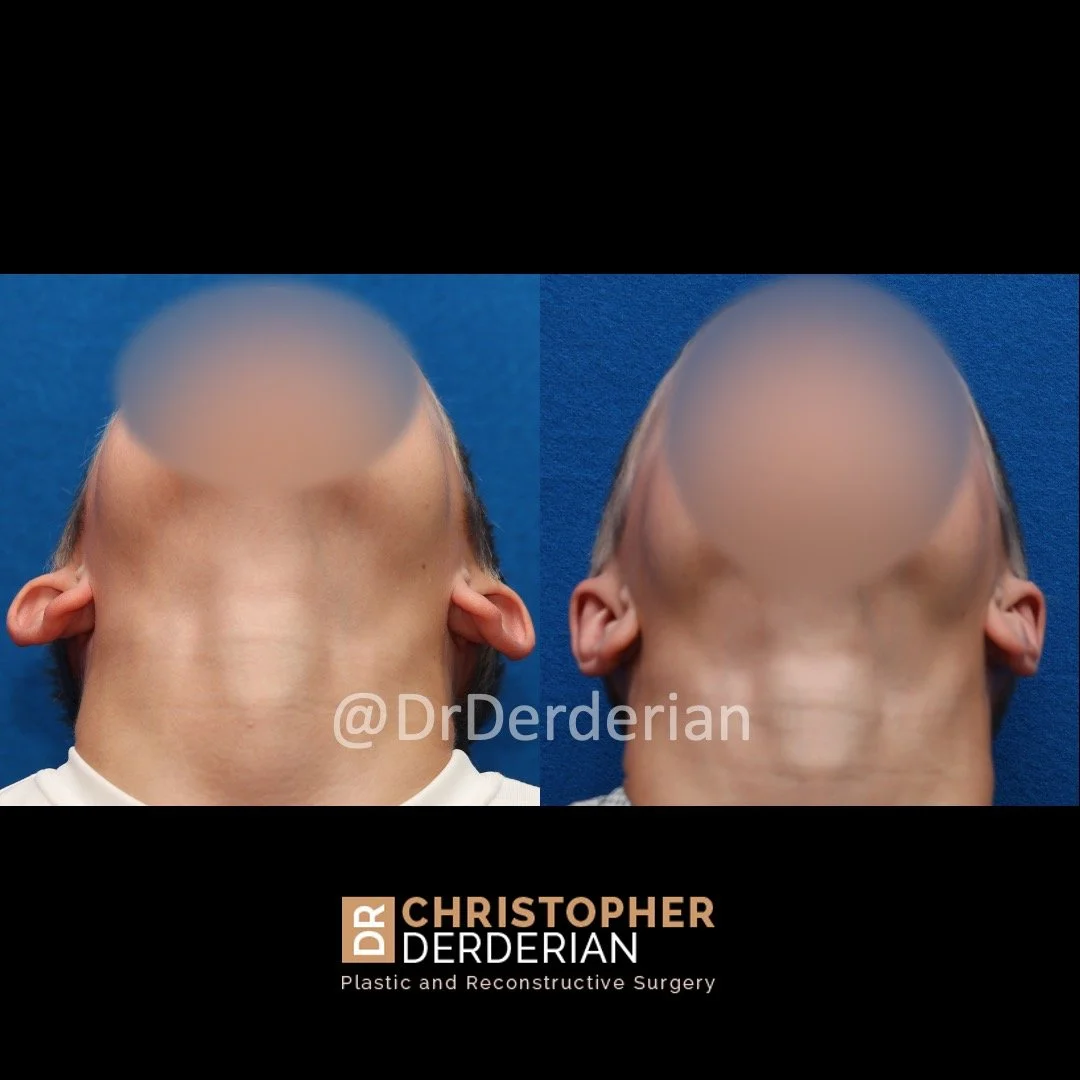
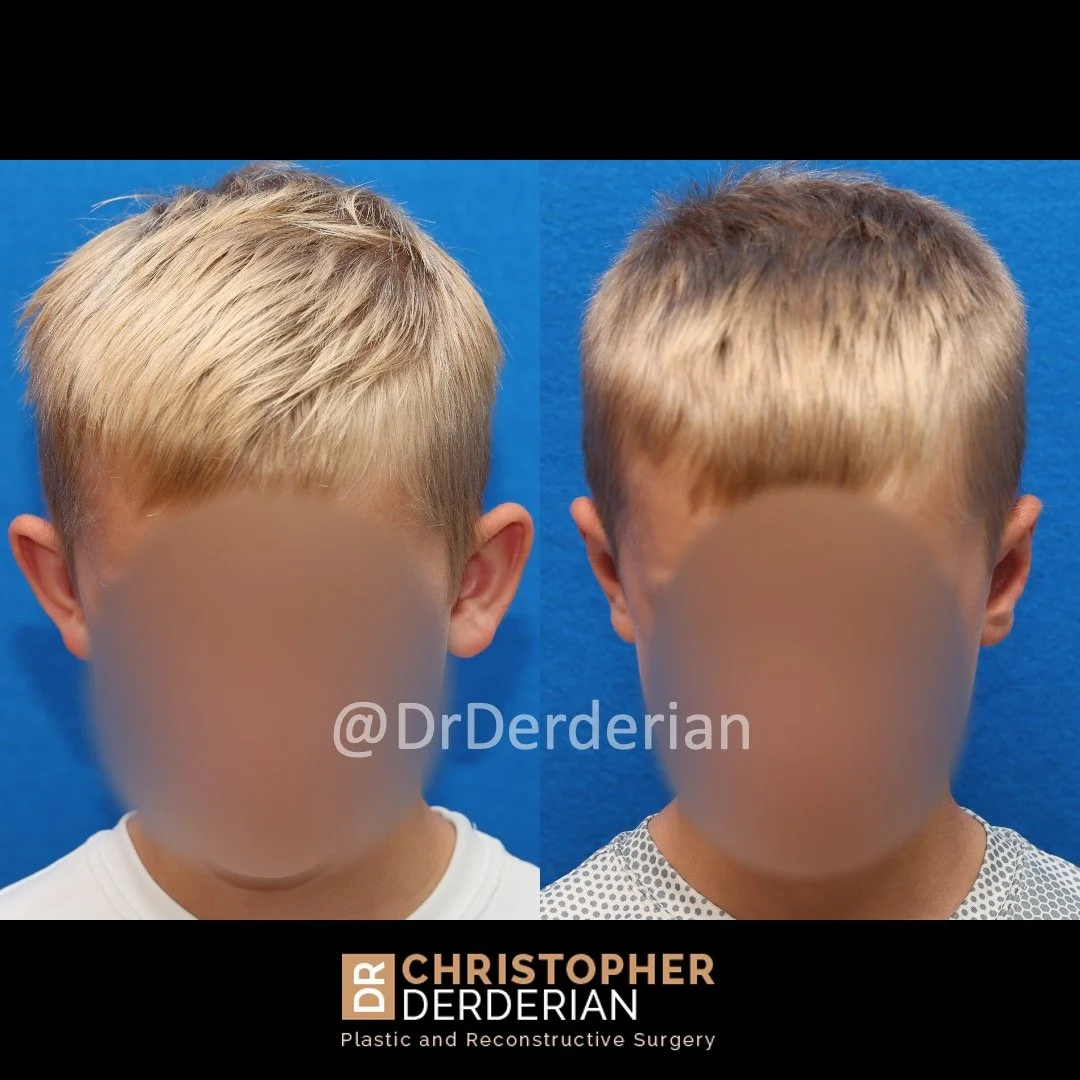
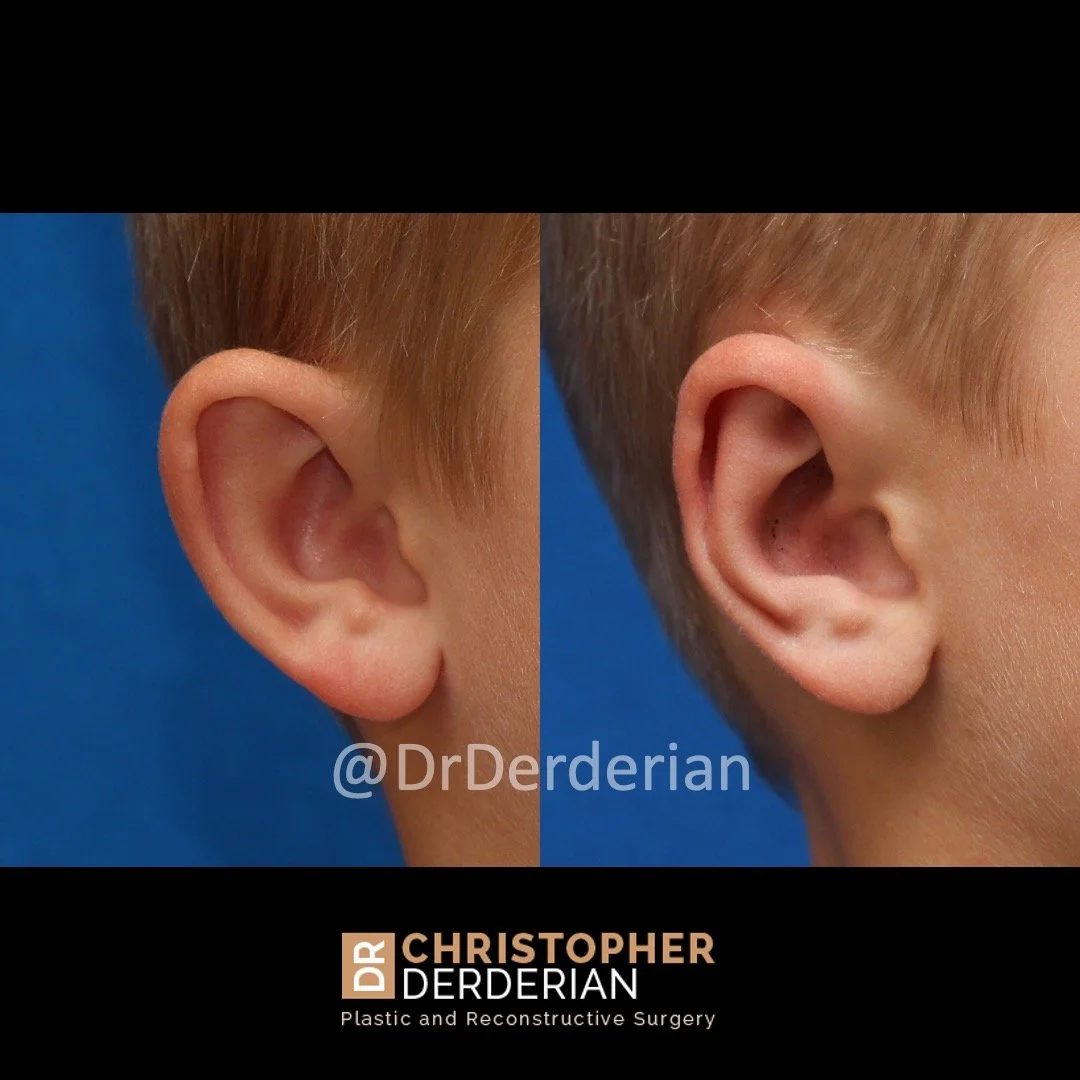
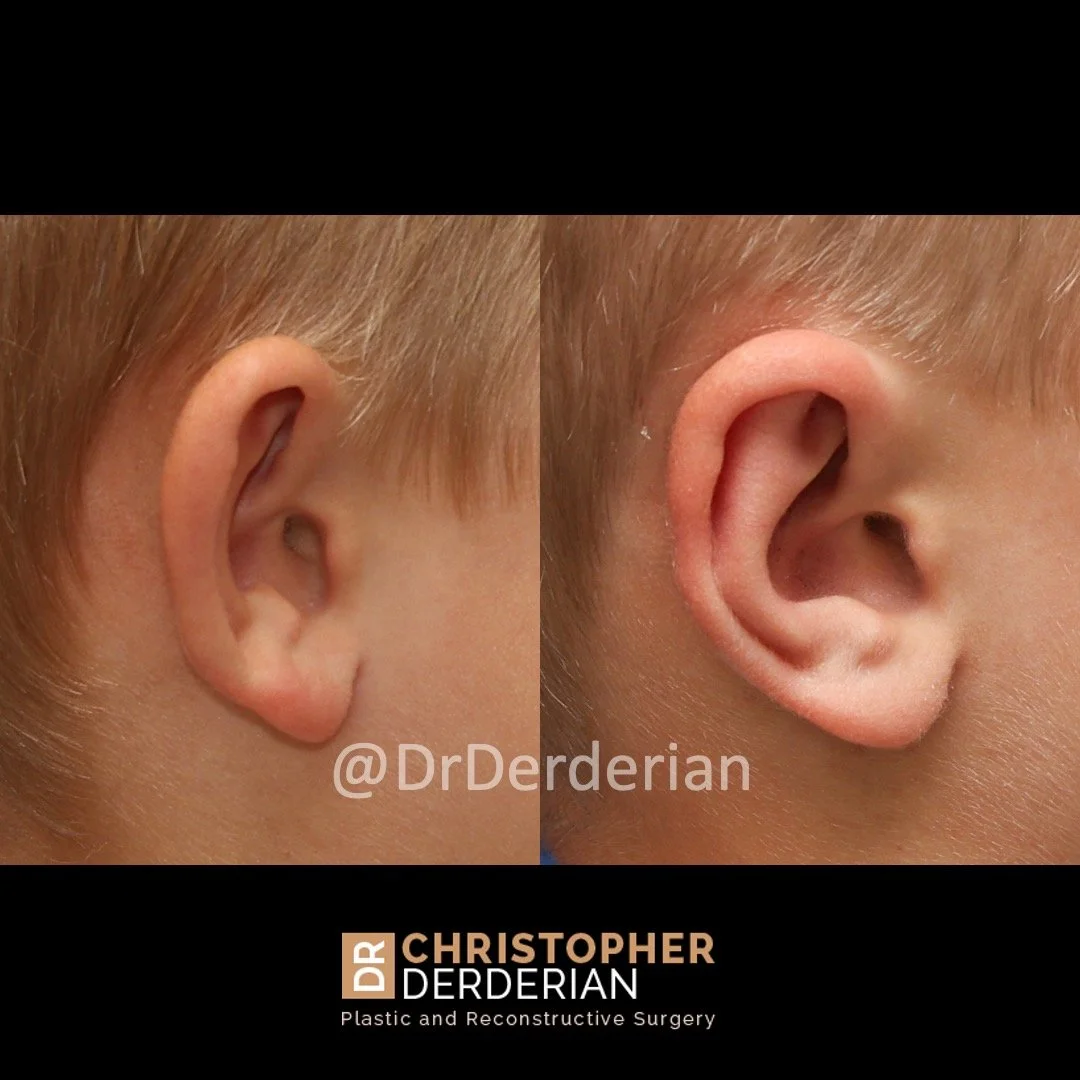
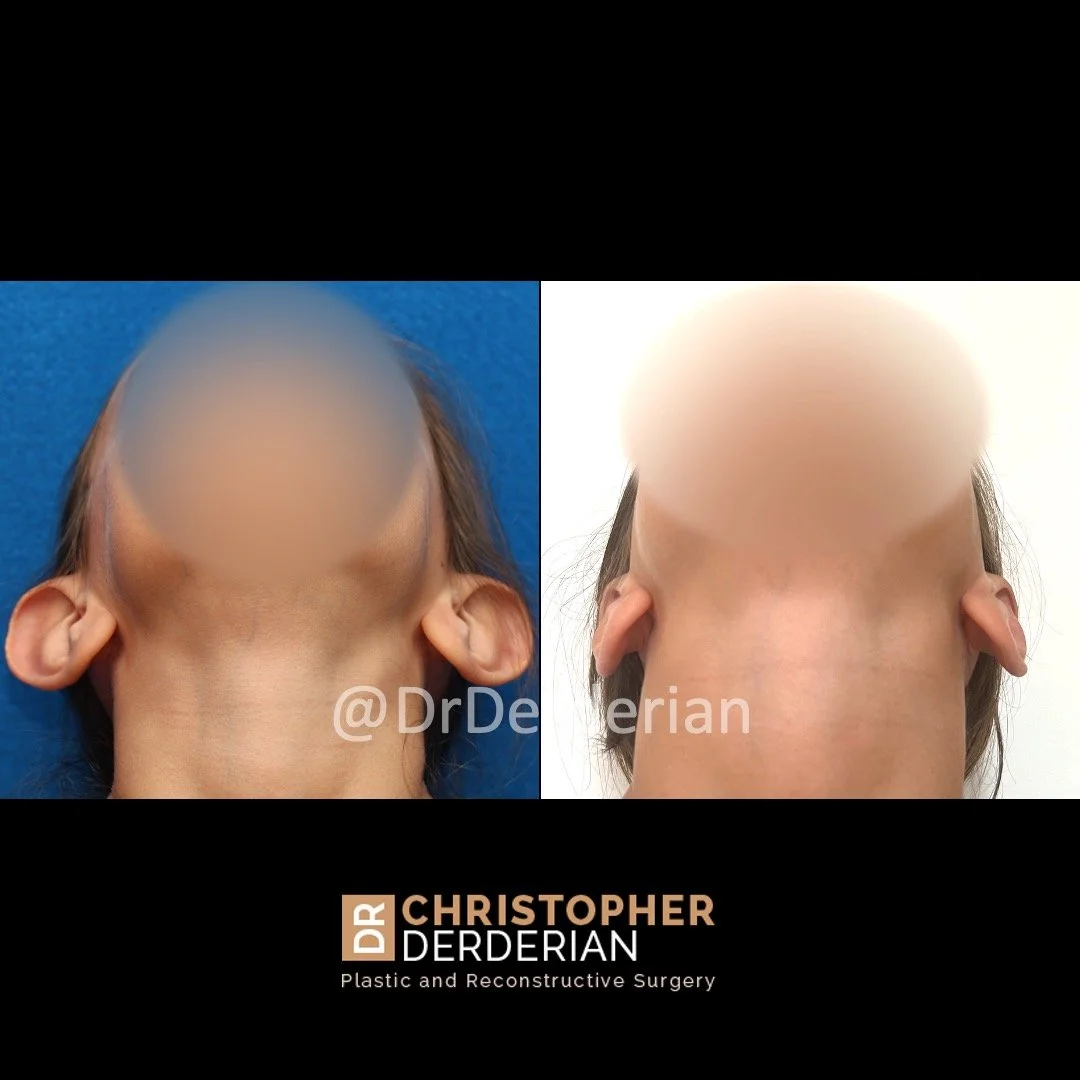
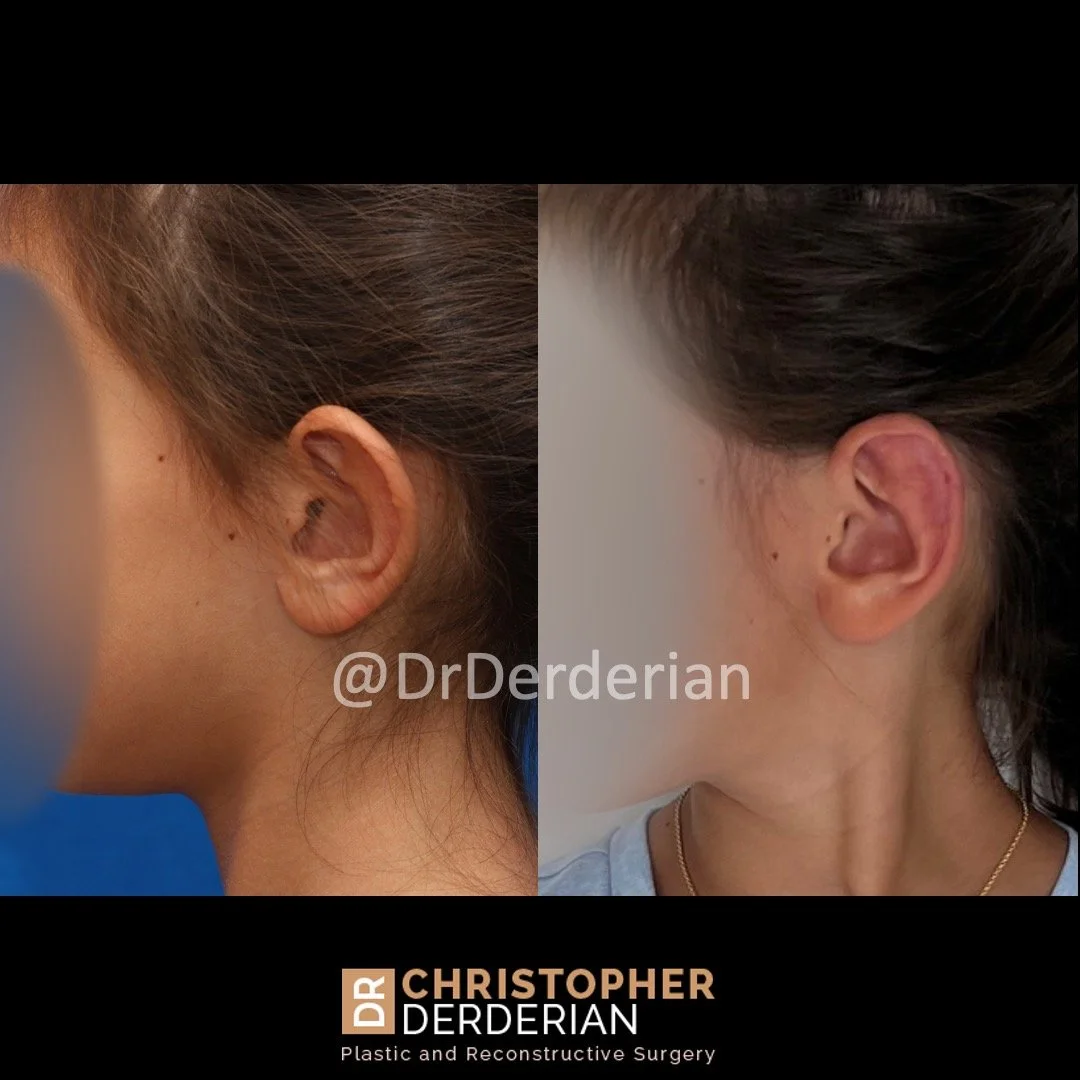
Otoplasty is a cosmetic ear surgery that improves the appearance of the ears by changing their projection, shape and/or size. Otoplasty (ear pinning) is most frequently used to treat ears that protrude away from the head or “stick out too far.”
Otoplasty can also be combined with procedures for ears that are disproportionately large (macrotia), called reduction otoplasty. Ears that draw unwanted attention are a frequent source of self-esteem issues for both children and adults. This commonly makes people with prominent ears so self conscious that they conceal their ears with their hair or avoid hairstyles or hats that accentuate the ears.
Dr. Derderian’s goals for your Otoplasty
Dr. Derderian performs a high volume of otoplasty and ear surgery procedures in his practice in Dallas. It is critical that the changes made to the ears with otoplasty have a natural appearance. Ears that have an “operated on” appearance with harsh or unnatural contours can be just as eye-catching as the original ear shape or projection. The goal is to take attention away from the ears and the best way to achieve that goal is to create a normal appearing ear that draws no attention. Otoplasty is not a “one size fits all” operation. Dr. Derderian’s extensive experience has allowed him to develop a large “toolbox” of surgical maneuvers to create a natural shape, projection and size to the ears while bringing balance and proportion to the ears and face. Inexperienced surgeons often apply the wrong operation to the ears that results in poor outcomes. This is just like the old saying, “when all you have is a hammer, everything looks like a nail!” Dr. Derderian customizes his approach to each patient based upon the anatomy of their ears and their goals.
-
Common concerns that can be treated with otoplasty include:
- Ears that “stick out too far”
- Overly large ears — a condition called macrotia
- Uneven ears – size or shape
- Unsatisfactory results from previous otoplasty
- Congenital ear malformations including constricted ear, lop ear and cryptotia
The ideal patient is healthy and does not use nicotine or have a medical conditions that can impair healing. It is important that the patient has a positive outlook and specific goals for improvement in their appearance.
In the case of children, I wait until at least age 5 years old to perform an otoplasty for two main reasons. It is important to allow the ear to grow close to the adult size to make sure that the correction from otoplasty will continue to look normal after growth of the ear is complete. At age 5 years old the child's ear is about 85% of the adult size. Otoplasty requires placement of stitches in the cartilage of the ear (under the skin) to reshape and reposition the ear. The cartilage of the ear is very soft and weak before age five years old. After age 5 years old the cartilage is strong enough to hold the sutures reliably that significantly increases the chance that the otoplasty will be successful.
Other considerations in terms of timing for surgery include the patient’s ability to be cooperative with the care required after surgery and the presence or absence of teasing from peers. In general we advocate for performing otoplasty before any issues with teasing arise. The incidence of teasing increases significantly after age 7.
-
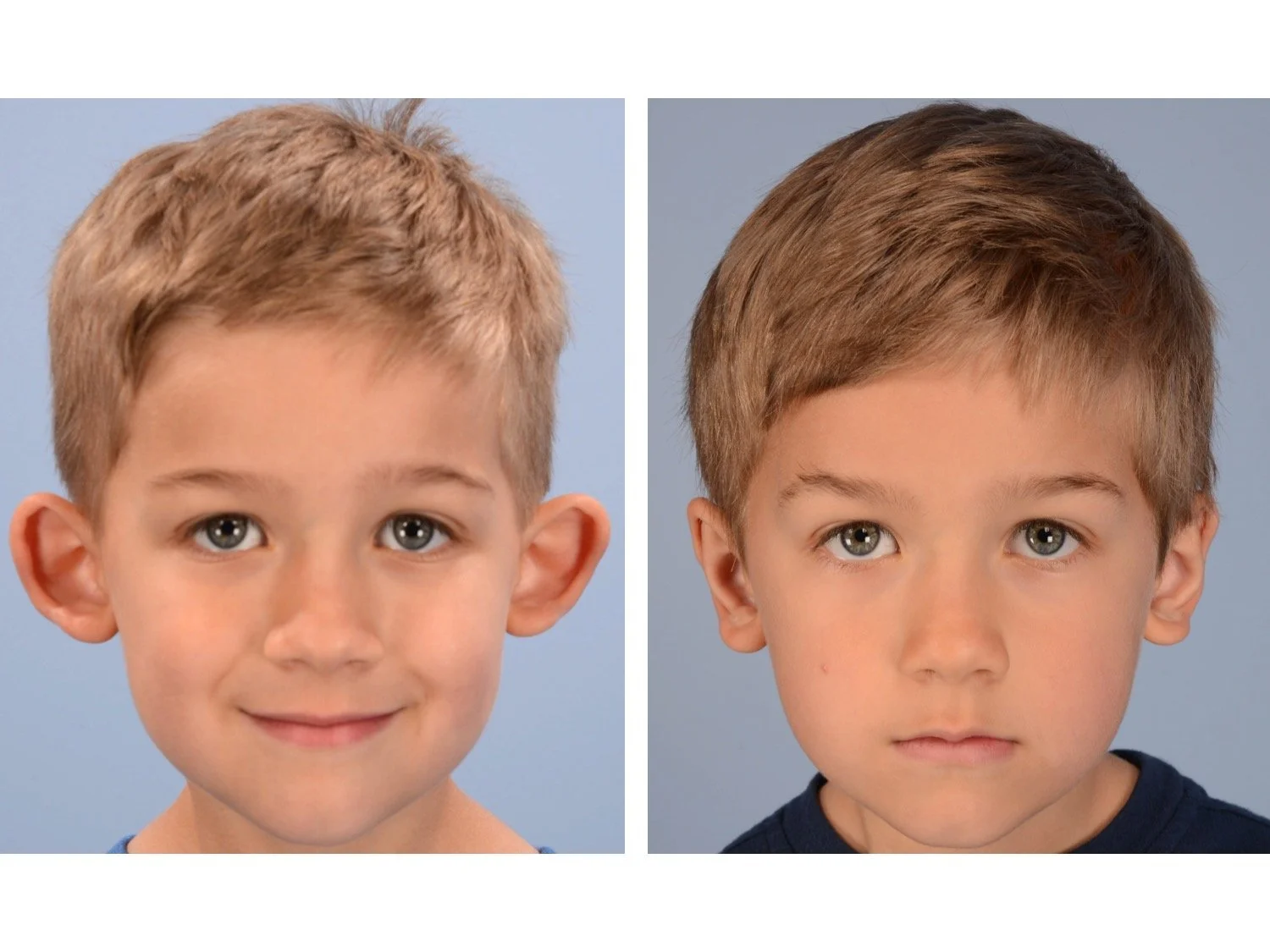
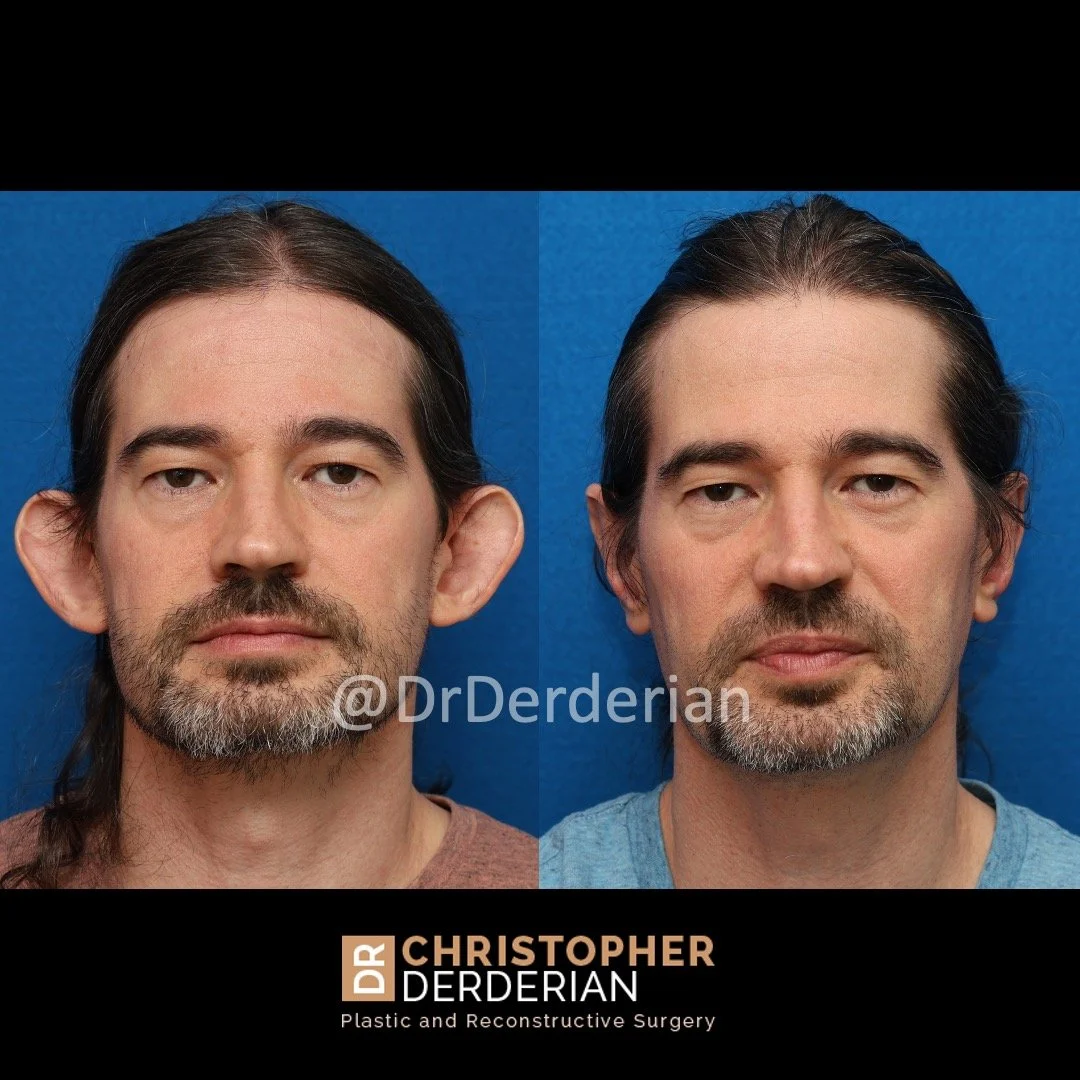
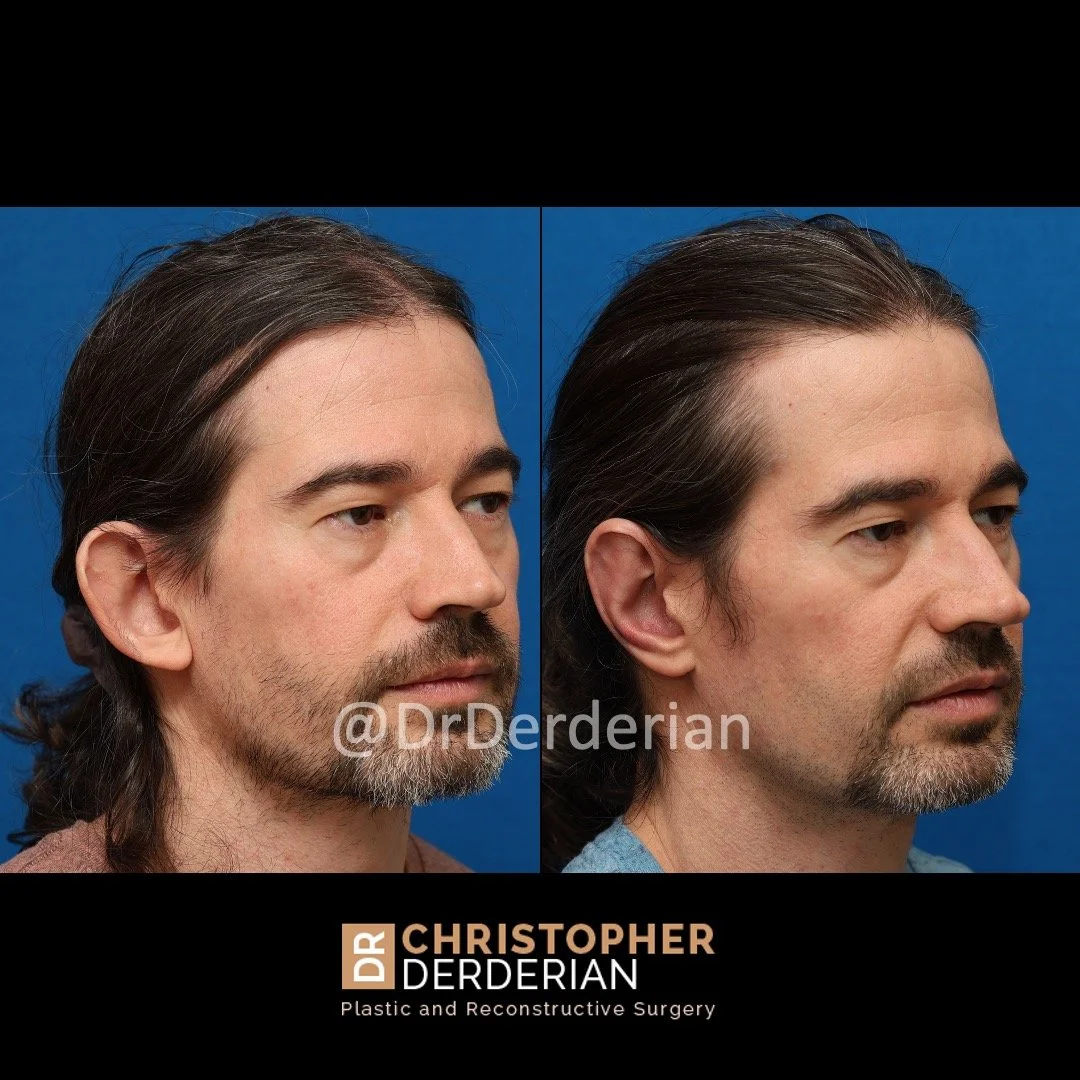
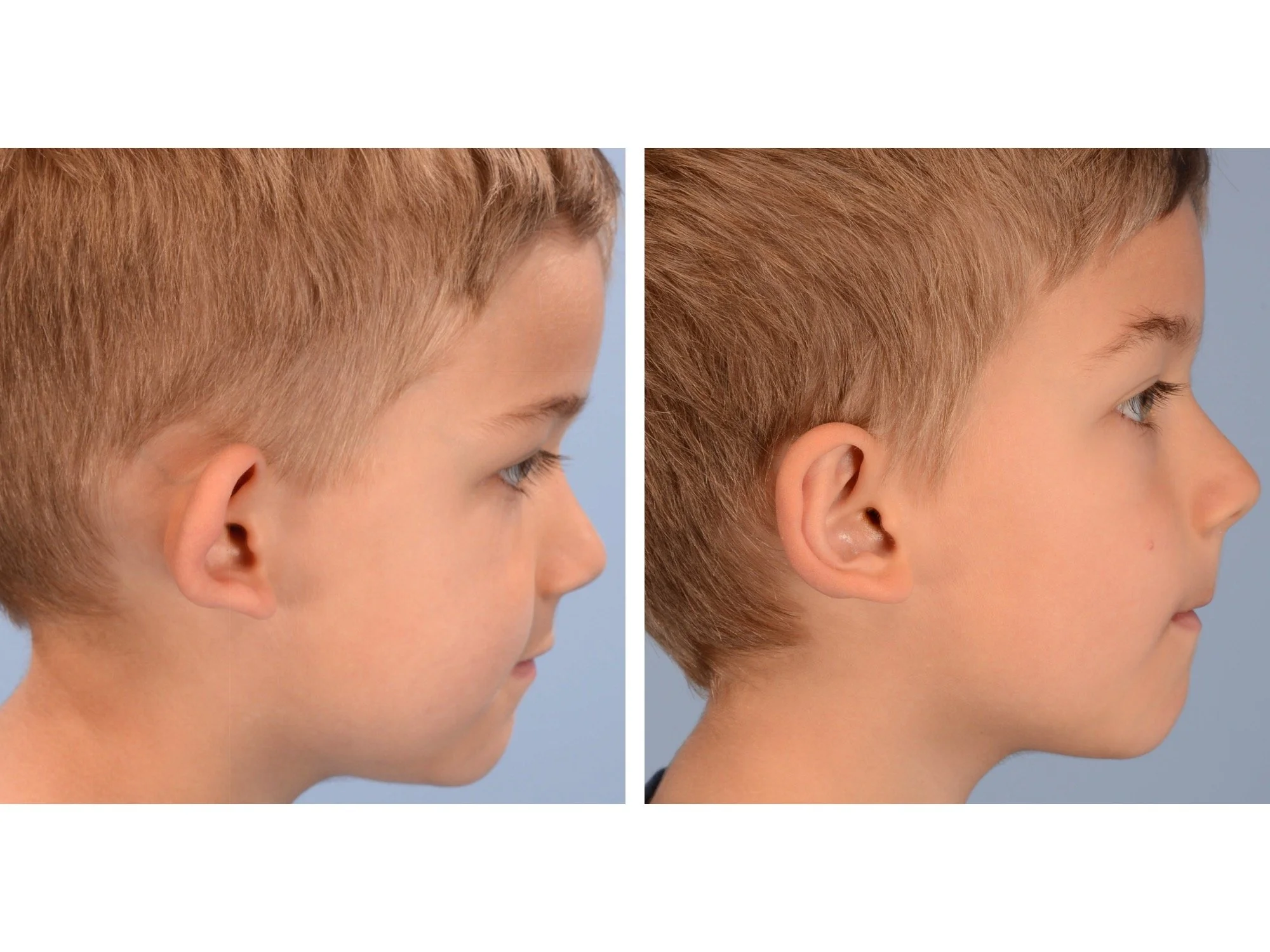
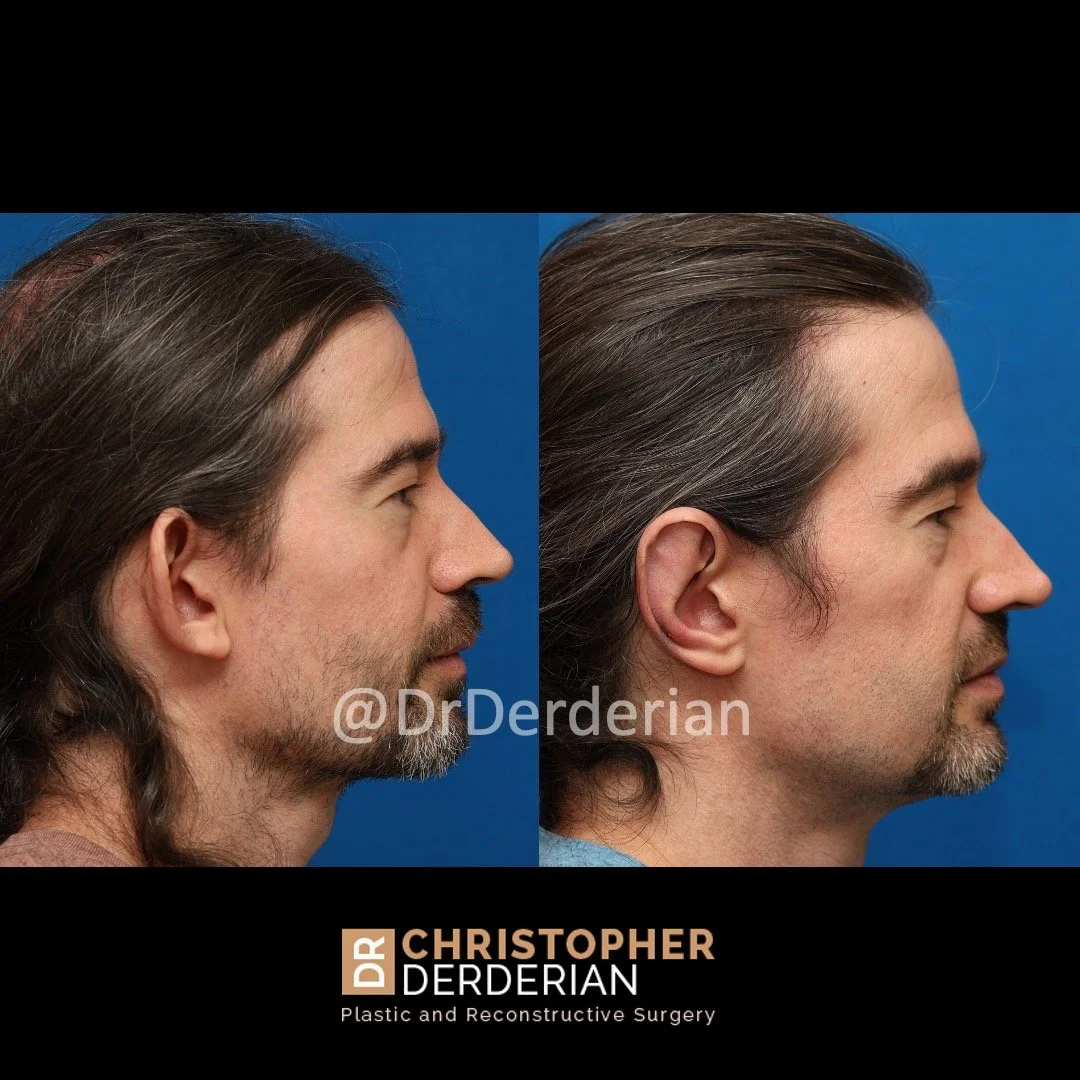
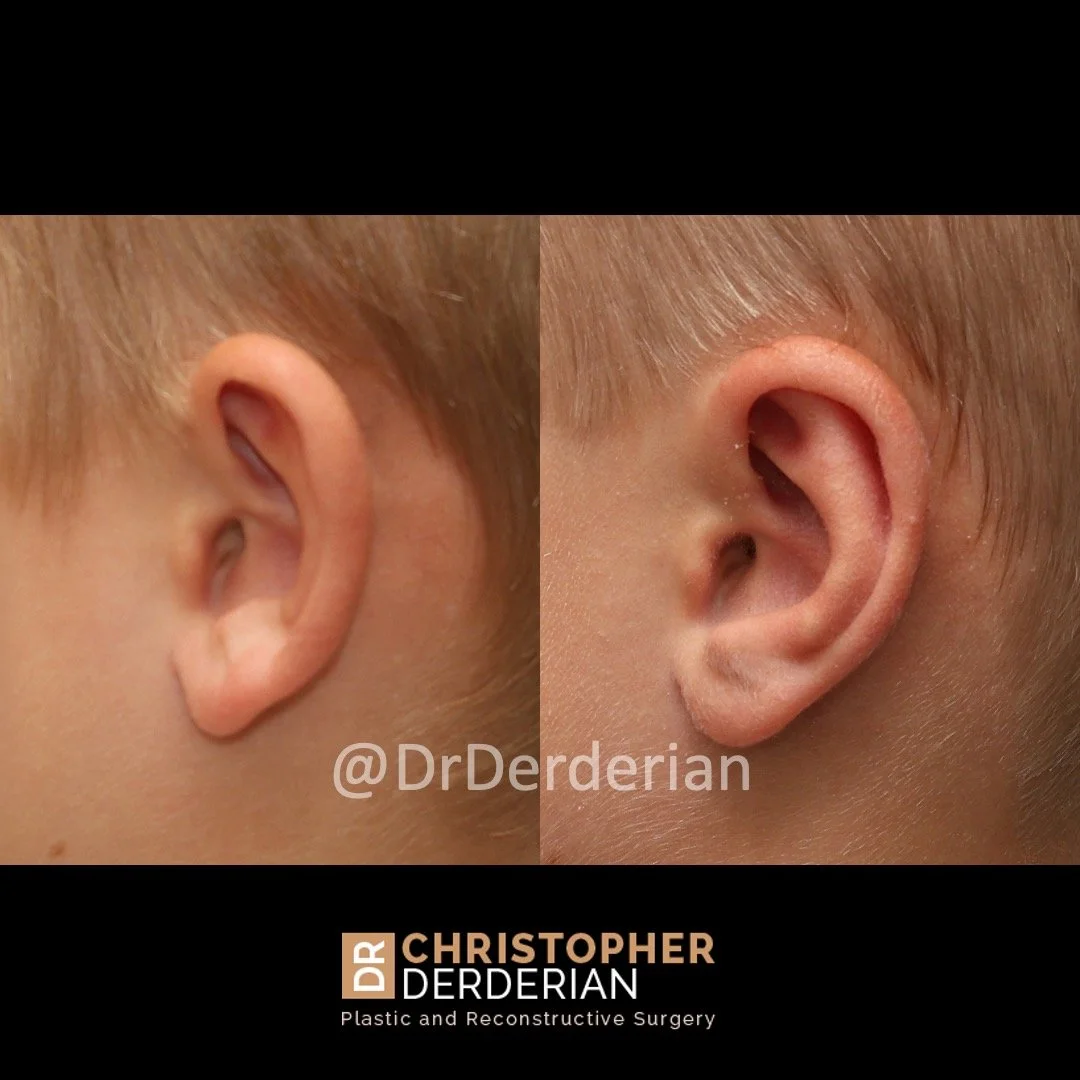
Prominent ear is the medical term for an ear that "sticks out too far." We all know people who have ears that stick out farther than the average person because it attracts the attention of one's eye. There are two primary causes for prominent ears. Loss of the delicate folds of the ear causes the outer rim (helical rim) of the ear to flare out and forward. Too much cartilage in the conchal bowl of the ear also causes the ear to be pushed out and forward. The most common scenario is that there is a combination of both loss of the normal antihelix fold and excess conchal cartilage.
-
Dr. Derderian will discuss your concerns about the appearance of your ears. A complete history and examination will be performed to ensure that you or your child is a good candidate for surgery. After verifying that you are a good candidate, Dr. Derderian will have a detailed discussion with you to explain his customized plan to improve the appearance of your ears.
-
ANESTHESIA
For most cases, general anesthesia will be used to provide the most comfortable patient experience. For minor changes in the ear shape, local anesthesia may be used. Dr. Derderian will make a recommendation on which anesthesia would be best for your case.
INCISIONS AND SCARS
The surgical maneuvers to create the natural folds of the ears or reduce projection of the ears can be performed through an incision in the groove between the back of the ear and the skull, so the scar will be well hidden. If incisions are needed on the front of the ear, they are placed within the natural folds of the ear so they will be hidden.
HOW DOES OTOPLASTY CHANGE THE SHAPE AND APPEARANCE OF EARS?
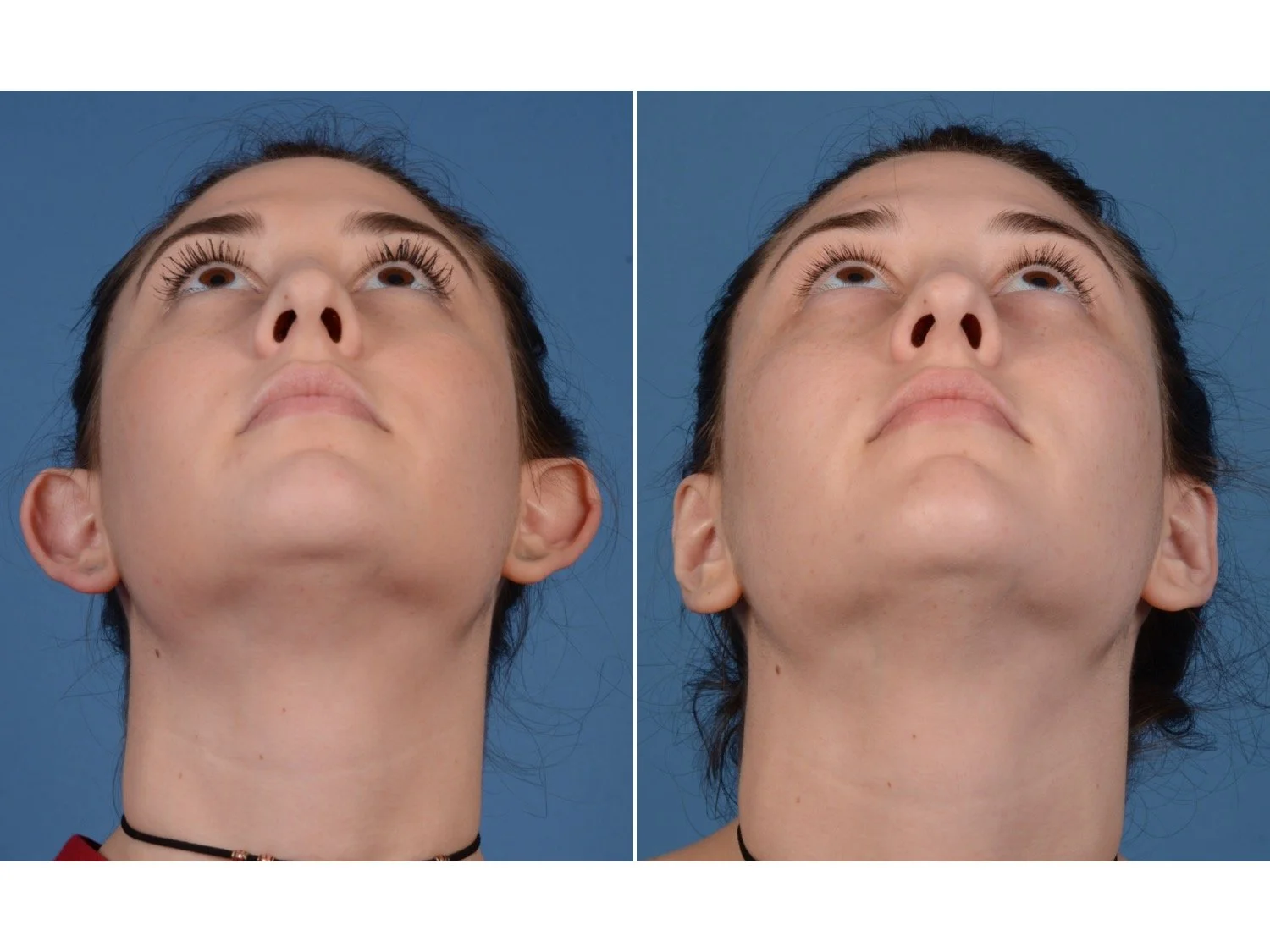
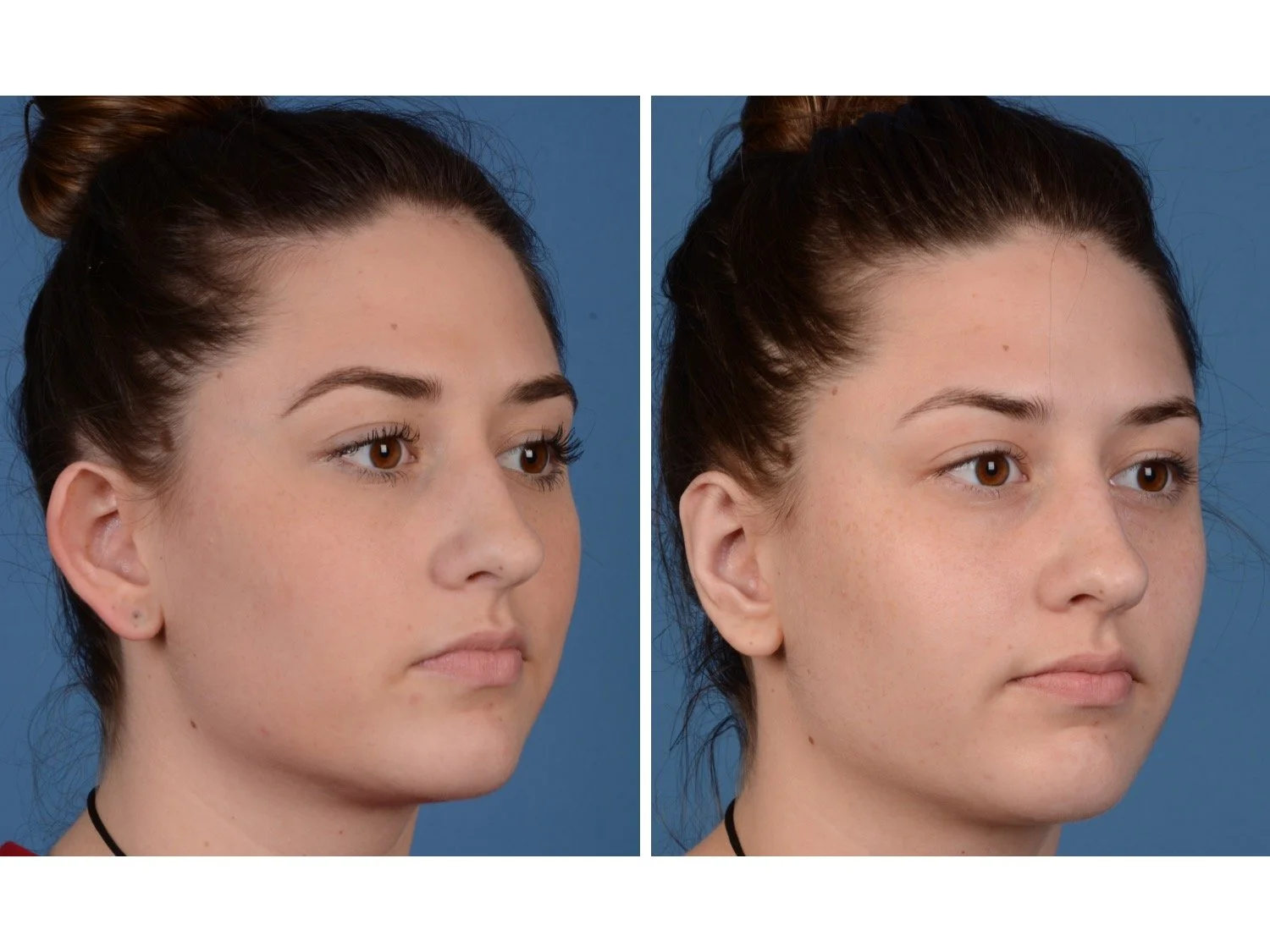
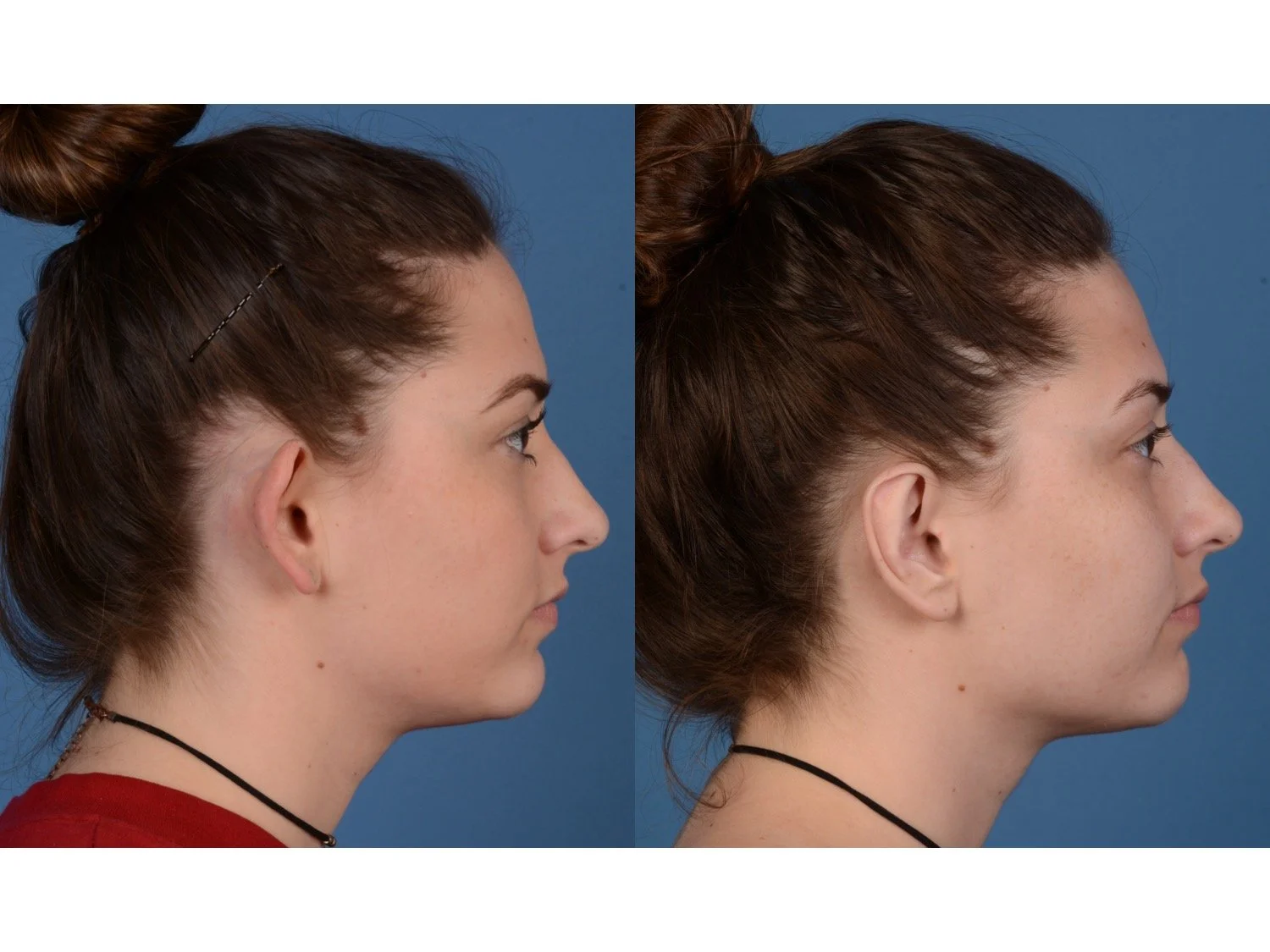
Otoplasty is a surgery that may require many different surgical maneuvers to improve the appearance of the ears. The maneuvers in the otoplasty will vary from patient to patient based on the anatomy of the ears, just as two peoples’ noses may require totally different operations to improve their appearance, but both operations would still be called a rhinoplasty (“nose job”). The cartilage is what gives the ear its shape. If there are missing folds of the ears, they are created using sutures (stitches) placed in the cartilage on the back of the ear to bend the cartilage and reshape it to create a natural and normal looking fold on the front of the ear. Additional sutures are also commonly used to rotate the ears back toward the head, into a normal projection and position. Occasionally, excision of excess cartilage from the conchal bowl may be needed to achieve normal projection. There are a number of other maneuvers that may also be used to refine the shape or decrease the size of the ears. Non-dissolvable sutures are used to create and secure the new shape or position of the ear cartilage because it takes about 1 year for the ear cartilage to permanently adapt to the new ear shape. Dissolvable sutures are used to close the skin incision on the back of the ear. The surgery takes about two and a half hours on average to correct both ears. The illustrations below show how the common maneuvers performed in otoplasty can change the shape and projection of the ears.
-
A large bulky dressing is placed in the operating room to protect the ears and keep the patient comfortable after otoplasty. This is worn for 3-4 days. Pain is prevented with prescribed pain medicine and ibuprofen. The prescribed pain medicine is typically needed for about 2-3 days, and only ibuprofen and tylenol are used as needed after that time. After the dressings are removed the hair can be washed and the ears can get wet. A Buff is used as a headband to be worn at night only for 3 months after surgery to protect the ears. Patients may return to school or work in 1-week and return to normal exercise and sports in 3 weeks.
-
After the dressings are removed the improvement in the shape and projection of the ears is immediately appreciated, despite the minor swelling that will be present. That swelling resolves quickly and the ears have a totally normal appearance by 3-4 weeks after surgery.
-
Any time an incision is made in the skin there is a risk for infection and scarring. As discussed above, the incisions are hidden in the crease between the ear and the skull on the back of the ear or in the folds on the front of the era so they are hidden. The skin is cleaned with an iodine solution and sterile drapes and intravenous antibiotics are given before the incision to prevent infection. It is possible to have residual prominence of the ears or contour irregularities after surgery. The incision sites may remain tender to touch for 4-6 weeks after surgery.
-
The cost of an otoplasty varies depending on the degree of the complexity of the surgery and the length of the procedure. Minor corrections of the shape and/or projection of the ears may be performed in the office under a local anesthetic. Office procedures start at $4,000. When more extensive procedures are needed, the total cost includes the fees for the surgeon, anesthesiologist and the surgical facility. The combined cost of otoplasty ranges from $8,000-11,000. Each surgery is customized to the goals of the patient and the patient’s unique anatomy. After your consultation, Dr. Derderian’s staff will provide a detailed quote to you with the exact cost for your surgery, and they will assist you with payment options and scheduling your procedure.
-
Dr. Derderian developed his interest for otoplasty and ear reconstruction early in his training, and ear surgery has been a focus of his surgical practice from day one. His passion for excellence in ear surgery has made otoplasty and ear reduction surgery a large part of his practice in Dallas. He performs a large number of otoplasty and related ear surgeries for both children and adults. Dr. Derderian is board certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery. He frequently lectures about otoplasty and has multiple publications related to ear surgery. Dr. Derderian has been selected annually as one of the top plastic surgeons in Dallas by D Magazine since 2015.